 CriglerNajjar syndrome type I is characterized by unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia resulting from an autosomal recessive inherited deficiency of hepatic UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) 1A1 activity. Elevated bilirubin formation due to increased RBC
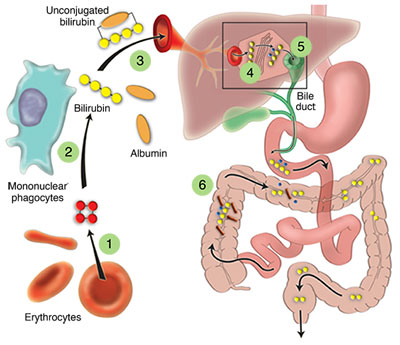
CriglerNajjar syndrome type I is characterized by unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia resulting from an autosomal recessive inherited deficiency of hepatic UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) 1A1 activity. Elevated bilirubin formation due to increased RBC  2 Bilirubin Conjugation Once in the liver, glucuronic acid is added to unconjugated bilirubin by the enzyme glucuronyl transferase.This forms conjugated bilirubin, which is soluble. This enzyme converts the toxic form of bilirubin (unconjugated bilirubin) to its nontoxic form (conjugated bilirubin), making it able to be dissolved and removed from the body. The bilirubin-UGT enzyme is primarily found in cells of the liver, where bilirubin glucuronidation takes place. At least 59 mutations have been It also changes some hormones, medicines, and toxins into non-harmful products. Laboratory tests for cholestasis include GGT, alkaline phosphatase, and 5 nucleotidase, of which GGT and alkaline phosphatase are most widely used. catherine viollon abadie studies Numerical Analysis and Scientific Computing, Botanique, and Corrosion Science. After delivery, the newborn's liver must clear the bilirubin on its own which can require several days. Glucuronyl transferase is a liver enzyme. An ALT test measures the amount of this enzyme in the blood. It also changes some hormones, medicines, and toxins into non-harmful products. What enzyme deficiency is it? Liver function tests (LFTs or LFs), also referred to as a hepatic panel, are groups of blood tests that provide information about the state of a patient's liver. Deficiency in bilirubin UDP-glucuronyl transferase as a genetic determinant of acetaminophen toxicity. The human liver bilirubin UDP-glucuronosyl transferase (bilirubin UDPGT) [EC 2.4.1.17] is responsible for the enzyme deficiency in Ascorbic acid deficiency and hepatic UDP-glucuronyl transferase. Although patients with the Crigler-Najjar syndrome (Type I) and Gunn rats lack UDP glucuronate glucuronyltransferase, their livers enzymatically convert bilirubin monoglucuronide to diglucuronide in vitro. A disorder characterized by the body's inability to metabolize galactose. How is bilirubin conjugated in the liver? The skin can take on a yellow color (jaundice) if the body does not produce enough glucuronyl transferase. Hong H, Johnson P: Antioxidant enzyme activities and lipid 28. Mukherjee AB; Krasner J Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol; 1979 Apr; 24(1):159-68. It also changes some hormones, medicines, and toxins into non-harmful products. describing bilirubin transport and metabolism in the liver have been validated solely by analysis of the plasma disappearance of radiolabeled bilirubin in hu-man subjects. Neumann, Catherine Mary. The level of free bilirubin in blood considerably exceeds the normal values.
2 Bilirubin Conjugation Once in the liver, glucuronic acid is added to unconjugated bilirubin by the enzyme glucuronyl transferase.This forms conjugated bilirubin, which is soluble. This enzyme converts the toxic form of bilirubin (unconjugated bilirubin) to its nontoxic form (conjugated bilirubin), making it able to be dissolved and removed from the body. The bilirubin-UGT enzyme is primarily found in cells of the liver, where bilirubin glucuronidation takes place. At least 59 mutations have been It also changes some hormones, medicines, and toxins into non-harmful products. Laboratory tests for cholestasis include GGT, alkaline phosphatase, and 5 nucleotidase, of which GGT and alkaline phosphatase are most widely used. catherine viollon abadie studies Numerical Analysis and Scientific Computing, Botanique, and Corrosion Science. After delivery, the newborn's liver must clear the bilirubin on its own which can require several days. Glucuronyl transferase is a liver enzyme. An ALT test measures the amount of this enzyme in the blood. It also changes some hormones, medicines, and toxins into non-harmful products. What enzyme deficiency is it? Liver function tests (LFTs or LFs), also referred to as a hepatic panel, are groups of blood tests that provide information about the state of a patient's liver. Deficiency in bilirubin UDP-glucuronyl transferase as a genetic determinant of acetaminophen toxicity. The human liver bilirubin UDP-glucuronosyl transferase (bilirubin UDPGT) [EC 2.4.1.17] is responsible for the enzyme deficiency in Ascorbic acid deficiency and hepatic UDP-glucuronyl transferase. Although patients with the Crigler-Najjar syndrome (Type I) and Gunn rats lack UDP glucuronate glucuronyltransferase, their livers enzymatically convert bilirubin monoglucuronide to diglucuronide in vitro. A disorder characterized by the body's inability to metabolize galactose. How is bilirubin conjugated in the liver? The skin can take on a yellow color (jaundice) if the body does not produce enough glucuronyl transferase. Hong H, Johnson P: Antioxidant enzyme activities and lipid 28. Mukherjee AB; Krasner J Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol; 1979 Apr; 24(1):159-68. It also changes some hormones, medicines, and toxins into non-harmful products. describing bilirubin transport and metabolism in the liver have been validated solely by analysis of the plasma disappearance of radiolabeled bilirubin in hu-man subjects. Neumann, Catherine Mary. The level of free bilirubin in blood considerably exceeds the normal values. Jaundice of Newborns (Hyperbilirubinemia) Physiological jaundice typically occurs because a newborns liver is immature and processes bilirubin more slowly, because the enzyme UDP-glucuronyl transferase is deficient. 2.4.1.17) catalyzes formation of bilirubin mono-glucuronide from bilirubin and UDPglucuronic acid. The product solubility in blood is increased allowing it to be eliminated from the body by the kidneys . A deficiency in the bilirubin specific form of glucuronosyltransferase is thought to be the cause of Gilbert's syndrome, which is characterized by unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia . Glucuronyl transferase is a liver enzyme . Cells from a clonal strain (MH 1 C 1) of rat hepatoma were transplanted subcutaneously into two homozygous Gunn rats, which are jaundiced because the enzyme bilirubin uridine diphosphate-glucuronyltransferase is absent from the liver. Ascorbic acid deficiency and hepatic UDP-glucuronyl transferase. There was a close correlation between the bilirubin glucuronyl-transferase activity as measured by two procedures, colorimetric and radioisotopic. It also changes some hormones, medicines, and toxins into non-harmful products.
UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1-1 also known as UGT-1A is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the UGT1A1 gene.. UGT-1A is a uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase (UDP-glucuronosyltransferase, UDPGT), an enzyme of the glucuronidation pathway that transforms small lipophilic (fat-soluble) molecules, such as steroids, bilirubin, hormones, and drugs, into
This condition is known as non-hemolytic jaundice.
A deficiency in dietary ascorbic acid has also been shown to result in a reduction in the specific activity of UDPGT towards ~-aminophenol 1131. Bilirubin glucuronoside glucuronosyltransferase (E.C. It changes bilirubin into a form that can be removed from the body through the bile . Slovnk pojmov zameran na vedu a jej popularizciu na Slovensku.
Gilbert syndrome is a hereditary disease that is characterized by a slight elevation in the levels of bilirubin in the blood caused by a mutation in a liver enzyme called glucuronyl transferase.
2 Bilirubin Conjugation. The microsomal enzyme uridine diphosphate (UDP) glucuronate glucuronyltransferase (E.C. This allows conjugated bilirubin to be excreted into the duodenum in bile.
A Gartner LM, Cohen M, Ezzer JB, Levi AJ. Thus, the liver cannot detoxify certain unwanted chemicals from the body due to deficiency of this enzyme.
Only when conjugated can bilirubin be actively excreted into the bile. Low Bilirubin Levels: Symptoms, Causes, and Potential Risks Deficiency of the enzyme glucuronyl transferase-lack of conjugation process of bilirubin in the liver, causing bilirubin to back up into the blood. The patient suffered from mild compensated haemolytic anaemia and excessive hyperbilirubinaemia (maximum concentration 581 mumol/l), the serum activity of The iron gets recycled, while biliverdin is reduced to create unconjugated bilirubin. Depending on the severity of deficiency, vitamin K may be supplemented orally or intramuscularly. Explore the latest full-text research PDFs, articles, conference papers, preprints and more on UGT. Results indicate that a genetic deficiency in bilirubin GT can be an important determinant of acetaminophen bioactivation and toxicity. The skin can take on a yellow color (jaundice) if the body does not produce enough glucuronyl transferase. School University of South Florida; Course Title GMS 6111; Uploaded By acf122. It also changes some hormones, medicines, and toxins into non-harmful products. Lysosomes contain hydrolytic enzymes, mainly proteases ( lysosomal enzymes) and acid phosphatase. The protein produced from the UGT1A1 gene, called the bilirubin uridine diphosphate glucuronosyl transferase (bilirubin-UGT) enzyme, is the only enzyme that glucuronidates bilirubin, a substance produced when red blood cells are broken down. The results suggest that the deficiency in Gunn rats and in the CriglerNajjar syndrome may be due to a structural defect in the microsomal matrix which contains glucuronyl transferase. Crigler-Najjar Syndrome Type I (Glucuronyl Transferase Deficiency) CN type I is a rare, autosomal recessive disease caused by homozygous or compound heterozygous mutations in theUGT1A1 gene which result in a premature stop codon or frameshift mutation and complete absence of UGT1A1 activity. Serum albumin binds bilirubin and carries it to the liver, where the newborn's transient deficiency of the enzyme glucuronyl transferase leads to reduced bilirubin conjugation. Glucuronyl transferase. In addition, newborns have a reduced amount of ligandin (a bilirubin binding protein), which assists with uptake of bilirubin into the liver cell. Upozornenie: Prezeranie tchto strnok je uren len pre nvtevnkov nad 18 rokov! The specific activities so measured were 19nmol of bilirubin `equivalents' conjugated/h per mg of protein and 16.918.4nmol of UDP-glucuronic acid incorporated/h per mg of protein, respectively. Gilbert's syndrome. It usually appears within a few days after birth and resolves within two weeks.
This rare inherited liver disorder is caused by deficiency of the enzyme glucuronyl transferase (UGT1A1), which catalyzes the conjugation of bilirubin (mainly to bilirubin diglucuronide) to render bilirubin water soluble. It changes bilirubin into a form that can be removed from the body through the bile. Irwin Arias. Available for iPhone, iPad, Android, and Web.
Neumann, Catherine Mary. This Paper. Glucuronyl transferase. Deficiency, UDP-glucuronosyltransferase: Underactivity of a liver enzyme that is essential to the disposal of bilirubin (the chemical that results from the normal breakdown of hemoglobin from red blood cells ). 142. For the first few days of life, the liver does not make adequate quantities of glucuronyl transferase. Deficiency, UDP-glucuronosyltransferase: Underactivity of a liver enzyme that is essential to the disposal of bilirubin (the chemical that results from the normal breakdown of hemoglobin from red blood cells ). We now have determined the trans-port kinetics of a bilirubin tracer pulse by analysis of plasma, liver, and bile radioactivity data from 30 intact rats. 1989. 1989. It is also possible that enterohepatic recirculation also occurs when parent drug in the bile is released from the gallbladder into the intestine and reabsorbed. Over 60% of the analgesic/antipyretic drug acetaminophen is eliminated by glucuronidation, which competes with a toxifying pathway involving cytochromes P-450-catalyzed bioactivation to a hepatotoxic reactive intermediate. Glucuronyl transferase is a liver enzyme. The skin can take on a yellow color (jaundice) if the body does not produce enough glucuronyl transferase. Disease Alternative Name A deficiency in the bilirubin specific form of glucuronosyltransferase is thought to be the cause of Gilbert's syndrome, which is characterized by unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia.