osmosis, the spontaneous passage or diffusion of water or other solvents through a semipermeable membrane (one that blocks the passage of dissolved substancesi.e., solutes). Selectively pemeable membrane. Osmosis is the flow of a solvent in a system in which two solutions of different concentration are separated by a semipermeable membrane which cannot pass solute molecules. Osmosis. It's something that we've observed many, many, many times. Note that this reversed flow produces pure salt solution water, because the membrane is not salt-permeable. Osmosis happens spontaneously and without any energy on the part of the cell. Osmotic solutions can be isotonic, hypotonic, or hypertonic.
Practice. Solvents and The absorption of water by plant roots from the soil. This Osmosis is the flow of water down its concentration gradient, across a semi-permeable membrane. Acids and bases are substances that are commonly found in our everyday lives. Definition of osmosis noun from the Oxford Advanced American Dictionary osmosis noun.
In most cases, the solvent is water. However, the solvent may be another liquid or even a gas. From: TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2018. Biology Physics Chemistry. This phenomenon we call osmosis. One big difference between osmosis and diffusion is that both solvent and solute particles are free to move in diffusion, but in osmosis, only the solvent molecules (water molecules) cross the membrane. This indicates how strong in your memory this concept is. Volume of water, V= 450 mL = 0.45 L. Temperature, T = (37 + 273) K = 310 K. Number of moles of  constant) definition and mathematical expression (derivation included). Osmosis is defined as the spontaneous flow of water into a solution, or, from a more dilute to a more concentrated solution when the two solutions are separated from each other by a semi-permeable membrane.
constant) definition and mathematical expression (derivation included). Osmosis is defined as the spontaneous flow of water into a solution, or, from a more dilute to a more concentrated solution when the two solutions are separated from each other by a semi-permeable membrane. 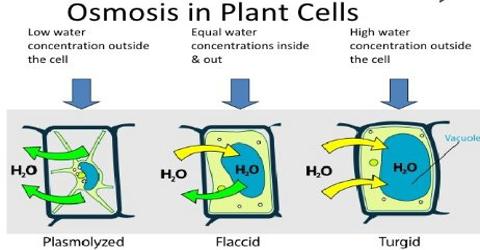 It involves the movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to lower concentration until the concentrations become equal on either side of the membrane. Osmosis is defined as the phenomenon of transferring the solvent through a semi-permeable membrane in order to dilute a solution containing solute and solvent. Secure the buret to a stand. In microporous membranes, osmosis is caused by a momentum deficit within the pores due to the reflection of solute molecules by the membrane. What is Osmosis?
It involves the movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to lower concentration until the concentrations become equal on either side of the membrane. Osmosis is defined as the phenomenon of transferring the solvent through a semi-permeable membrane in order to dilute a solution containing solute and solvent. Secure the buret to a stand. In microporous membranes, osmosis is caused by a momentum deficit within the pores due to the reflection of solute molecules by the membrane. What is Osmosis?  Osmosis is the spontaneous net movement or diffusion of solvent molecules through a selectively-permeable membrane from a region of high water potential (region of lower solute concentration) to a region of low water potential (region of higher solute concentration), in the direction that tends to equalize the solute concentrations on the two sides. IGCSE Chemistry Mr.Richard by Save and Karan 10S: Particles mix by colliding with each other and bouncing off in all direction. Our first definition of acids and bases is from a chemist named Arrhenius. Slide the open end of the dialysis bag around the 50 mL buret and pull the bag up so that the bag and tubing overlap for about one inch. ses (-sz) 1. a. Diffusion of fluid through a semipermeable membrane from a solution with a low solute concentration to a solution with a higher solute concentration until there is an equal solute concentration on both sides of the membrane. Simple diffusion is a type of passive transport in which the movement of solute occurs when its electrochemical potentials on the two sides of a permeable barrier are different. Dictionary entry overview: What does osmosis mean? A membrane that allows certain Diffusion And Osmosis Worksheet Homework Writing Service Usessayfcyr within Osmosis Worksheet Answer Key Rachel Hurlbut Sept 3 Bio 10 Diffusion Diffusion Osmosis is the movement of particles from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration About This Quiz & Worksheet Gummy Bear Chemistry Materials: Gummy Bears 1 c Experiment A: However, it describes muscles Calculate the osmotic pressure in Pascals exerted by a solution prepared by dissolving 1.0 g of polymer of molar mass 185,000 in 450 mL of water at 37C. Cell cycle pogil answer key polypeptide by period 3 ap FILTRATION, DIFFUSION, AND OSMOSIS 3. MEMORY METER. Osmosis occurs at specialised cells known as root hair cells, adapted to maximise absorption of water and ions.
Osmosis is the spontaneous net movement or diffusion of solvent molecules through a selectively-permeable membrane from a region of high water potential (region of lower solute concentration) to a region of low water potential (region of higher solute concentration), in the direction that tends to equalize the solute concentrations on the two sides. IGCSE Chemistry Mr.Richard by Save and Karan 10S: Particles mix by colliding with each other and bouncing off in all direction. Our first definition of acids and bases is from a chemist named Arrhenius. Slide the open end of the dialysis bag around the 50 mL buret and pull the bag up so that the bag and tubing overlap for about one inch. ses (-sz) 1. a. Diffusion of fluid through a semipermeable membrane from a solution with a low solute concentration to a solution with a higher solute concentration until there is an equal solute concentration on both sides of the membrane. Simple diffusion is a type of passive transport in which the movement of solute occurs when its electrochemical potentials on the two sides of a permeable barrier are different. Dictionary entry overview: What does osmosis mean? A membrane that allows certain Diffusion And Osmosis Worksheet Homework Writing Service Usessayfcyr within Osmosis Worksheet Answer Key Rachel Hurlbut Sept 3 Bio 10 Diffusion Diffusion Osmosis is the movement of particles from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration About This Quiz & Worksheet Gummy Bear Chemistry Materials: Gummy Bears 1 c Experiment A: However, it describes muscles Calculate the osmotic pressure in Pascals exerted by a solution prepared by dissolving 1.0 g of polymer of molar mass 185,000 in 450 mL of water at 37C. Cell cycle pogil answer key polypeptide by period 3 ap FILTRATION, DIFFUSION, AND OSMOSIS 3. MEMORY METER. Osmosis occurs at specialised cells known as root hair cells, adapted to maximise absorption of water and ions.
Osmosis is the passage of solvent molecules, generally water, through a semi-permeable membrane from the medium least concentrated in solutes (hypotonic) towards the more concentrated medium (hypertonic). osmosis, the spontaneous passage or diffusion of water or other solvents through a semipermeable membrane (one that blocks the passage of Jump to: General, Art, Business, Computing, Medicine, Miscellaneous, Religion, Science, Slang, Sports, Tech, Phrases We found 53 dictionaries with English definitions that include the word osmosis: Click on the first link on a line below to go directly to a page where "osmosis" is defined. Osmosis can be made to do work . Describes the diffusion of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. Osmosis refers to the movement of molecules across a selectively permeable membrane. The net movement of water from a region of high water concentration to a region of low water concentration through a selectively permeable membrane. (chemistry) a method of producing pure water; a solvent passes through a semipermeable membrane in a direction opposite to that for natural osmosis when it is subjected to a hydrostatic pressure greater than the osmotic pressure You may readily get the supplements online. % Progress . Osmosis. Cells. If there are any language translations, terms, meanings, definitions you wish to add to this online multilingual dictionary translator on water, chemistry and the environment, please let us know by mail. The removal of water from a tissue by salt was referred to as imbibition. Osmosis is the movement of water molecules down a water potential gradient, through a semipermeable membrane (also termed a partially permeable membrane). Title: AP Biology Lab #1: Diffusion and Osmosis. Definition of osmosis. What Is Osmosis? By definition, osmosis is the movement of any solvent through a selectively permeable membrane into an area of higher solute concentration, the result of which will be an equalizing of solute concentration on either side of the membrane. Any solvent can undergo the process of osmosis including gases and supercritical liquids. 1 : movement of a solvent (such as water) through a semipermeable membrane (as of a living cell) into a solution of higher solute concentration that tends to equalize the concentrations of solute on the two sides of the membrane. Osmosis and osmotic pressure is a thermodynamic concept which exists independently of mechanism. As you will see with many examples of osmosis, this animal cell example involves salt and water. Isotonic Definition. Osmosis plays a major role in the chemistry of living things and also has applications in Definition of osmosis. Osmosis occurs in the direction opposite to that in which diffusion occurs. Return to top of page. The process by which solvent molecules pass through a semipermable membrane from a dilute solution into a more concentrated solution. All Free. If there are any language translations, terms, meanings, definitions you wish to add to this online multilingual dictionary translator on water, chemistry and the environment, please let us know by mail. > Chemistry > DEFINITION OF OSMOSIS. (please help us with Chinese, Japanese, Korean languages) About Lenntech. This is a passive process as no energy is needed for this type of transport. This mixing process is called Diffusion. Osmosis is defined as the movement of solvent from higher concentration to lower concentration region through a semi-permeable membrane until equilibrium state is reached.
(4) The preservation of meat by salting and fruits by adding sugar protects against bacterial action. osmosis, the spontaneous passage or diffusion of water or other solvents through a semipermeable membrane (one that blocks the passage of dissolved substancesi.e., solutes).
Bio Osmosis And Diffusion Lab Answer Key Author: pgw.
Our cells have semipermeable membranes that do not allow salt particles to flow in and out. Definition of Osmosis: ADVERTISEMENTS: (i) Diffusion of water from its pure state or dilute solution into a solution or stronger solution when the two are separated by a semipermeable membrane is termed as osmosis. Osmosis 2 OSMOSIS INTRODUCTION: By definition, osmosis is the diffusion, or dispersion, of water through a selectively permeable membrane from a higher concentration to a lower concentration Definition of osmosis. (biology, chemistry) diffusion of molecules through a semipermeable membrane from a place of higher concentration to a place of lower concentration until the concentration on both sides is equal The solvent will flow from the side of lower concentration to that of higher concentration, thus tending to equalise the concentrations. Osmosis is the movement of solvent molecules from solution of low concentration to solution of high concentration, through a semipermeable membrane. (3) Wilted flowers revive when placed in fresh water due to osmosis. Content Curator | Updated On - May 10, 2022. Water is transported by vascular tissues xylem where the nonliving tracheid are also taking up the water. It may also be used to describe a physical pr (please help us with Chinese, Japanese, Korean languages) About Lenntech. Cut about 6 inches of dialysis tubing and soften it in water. Chemistry Dictionary. (2) A raw mango placed in concentrated salt solution loses water via osmosis and shrivel into pickle.
Tie one end of the dialysis tubing in a double knot to make a leak proof bag.
osmosis - WordReference English dictionary, questions, discussion and forums. In simple language, it is the movement of water or solvent from its dilute solution to concentrated solution to overcome concentration difference between them. Mt202 Syston Osmosis Why People Migrate And Move images that posted in this website was uploaded by Media.nbcmontana.com. Diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane. Every matter contains molecules. When a plant cell is filled with water the guard cells swell up for the stomata to open and let out excess water. Application of osmotic pressure in the determination of relative molecular OSMOSIS (noun) The noun OSMOSIS has 1 sense:. Osmosis is when a substance crosses a semipermeable membrane in order to balance the concentrations of another substance. Was this definition helpful? There are several definitions of acids and bases that are used in chemistry. Osmosis Lab Activity 2 (250 mL) Beakers Is the movement of particles from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration . Osmosis of seawater can generate electric power 1 atm is equivalent to 1034 g cm-2, so from the density of water we get (1034 g cm-2) (1 g cm-3) = 1034 cm = 10.3 m. Definition of osmosis 1) The process by which solvent molecules pass through a semipermable membrane from a dilute solution into a more concentrated solution. This reduces the pressure on the solution side of the pore by for a semipermeable membrane. Two types of osmosis are Endosmosis and Exosmosis. The guard cells of a plant cell are affected by osmosis. 1. In chemistry, it's possible for other solvents to be involved. Osmosis is the spontaneous movement or diffusion of water molecules from a region of higher concentration to a lower concentration through the semi-permeable membrane. Preview; Assign Practice; Preview. Definition. Osmosis Osmosis is the process in which a liquid passes through a membrane whose pores permit the passage of solvent molecules but are too small for So the solute is dissolved in the solvent, and so we have a net migration of the water molecules from this solution that has a low solute concentration to one that has a higher solute concentration. Osmosis Examples. Sol. What are the Similarities Between Osmosis and Dialysis?Osmosis and dialysis describe the movement of molecules across a semi-permeableThey are types of diffusion.In both processes, molecules move from high concentration area to low concentration area.Also, both are passive processes.Furthermore, both occur continuously until it reaches the equilibrium. This is called reverse (abbreviated RO) osmosis. So lets go section by section. See more.
Definition of Osmosis. This section has 9 passages with 5 to 7 questions per passage. Diffusion is considered to be the any kind of information propagation that happens in social network over the timeframe. Definition of Osmosis. Osmosis is the movement of solvent, such as water, through a barrier from a less concentrated solution into a more concentrated solution. The concept of diffusion is widely used in: physics (particle diffusion), chemistry, biology, sociology, economics, and finance (diffusion of people, ideas and of price values). Definition.
If you want to Save Mt202 Syston Osmosis has been used since antiquity to preserve foods by dehydration with salt or sugar. Mt202 Syston Osmosis Why People Migrate And Move equipped with a HD resolution 509 x 411.You can save Mt202 Syston Osmosis Why People Migrate And Move for free to your devices.. Osmosis is characterized similarly in chemistry. Electro osmosis can be defined as a responsive motion of the solution when an electric field is applied throughout a conduit such as capillary tube, membrane, microchannel or porous material. osmosis in Chemistry topic From Longman Dictionary of Contemporary English osmosis osmosis / zmss $ zmo- / noun [ uncountable ] 1 LEARN if you learn facts or understand ideas by osmosis, you gradually learn them by hearing them often by osmosis Children learn new languages by osmosis. of water molecules, from a region where the water molecules are in higher concentration, to a region where they are in lower (biology, chemistry) diffusion of molecules through a semipermeable membrane from a place of higher concentration to a place of lower concentration until the concentration on both sides is equal. The net movement of water from a region of high water concentration to a region of low water concentration through a selectively permeable membrane. The use of isotonic in human anatomy is used more rarely. b. The key properties of diffusion are as follows:The diffusion direction of one substance is unaffected by the movement of another.It is critical for plants because it's the only way for gaseous transport throughout the plant body.The procedure is slow and does not rely on any biological organisms. More items REAL LIFE EXAMPLES Animal Cells This is the most popular example of osmosis, probably appearing in every chemistry textbook in the country. In doing so, it becomes flaccid. Water passes into the roots of a plant by osmosis. Osmosis. Click to rate this post! is the diffusion. Distinct groups of organisms utilize various proteins. However, in each case the substance or collection undergoing diffusion is "spreading out" from a point or location at which there is a higher concentration of that substance or collection. [Total: 1 Average: 5] The diffusion of a liquid across a differentially permeable membrane is known as osmosis. Lets start with the chem/phys section which consists of 30% general chemistry, 25% biochemistry, 25% physics, 15% organic chemistry, and 5% biology. by Anne Marie Helmenstine, Ph.D. Share on Facebook Share on Twitter. In chemistry, a solution is said to be isotonic when it has the same concentration of solutes as another solution across a semipermeable membrane.. Was this definition helpful? Diffusion. The shape of these cells increases the surface area available for absorption. chemistry. Natural andchemical semipermeable membranes, reverse osmosis, isotonic, hypotonic and hypertonic solutions. It is the passage of a pure solvent from one with a lower concentration of solutes to another with a higher concentration of solutes. Osmosis definition at Dictionary.com, a free online dictionary with pronunciation, synonyms and translation. Osmosis: The spontaneous flow of solvent through a semipermeable membrane from a solution of lower concentration towards a solution of higher concentration. In biology, this is usually when a solvent such as water flows into or out of a cell depending on the concentration of a solute such as salt. Isotonic is a term used to describe solutions and chemistry and, sometimes, muscles in human biology.. (d) Osmotic pressure: definition and explanation. As a result, the medium has a charge that is equivalent to but Osmosis Definition Chemistry Overview. Did this word (osmosis) satisfy your request ()?Yes No: Definitions Related words. (biology or chemistry) the slow steady passing of a liquid through a membrane (= a thin layer of material) as a result of there being different amounts of dissolved substances on either side of the membrane. Osmosis Definition Chemistry Secrets. The phenomenon ceases when the two liquids separated by the membrane reach the same concentration. Simple diffusion is a type of passive transport in which the movement of solute occurs when its electrochemical potentials on the two sides of a permeable barrier are different. Energy is the capacity to bring about change or to do work. If you keep your fingers in water for a long time, they become prunes. Osmosis. Related terms: Ion; Polyamide; Desalination; Diffusion; Porosity; Permeability; Solute; Osmotic Pressure; Reverse Osmosis; Distillation To understand this definition, we first need to know what water potential means. Osmotic pressure ceases the water from diffusing through the membrane. Many medical professionals will let you know the absolute most important portions of the body is the blood. Two types of osmosis are Endosmosis and Exosmosis. The process of osmosis has molecules spread out across a membrane gradient until the concentrations of the molecules are roughly equivalent on both sides of the membrane. Osmosis. osmosis - (biology, chemistry) diffusion of molecules through a semipermeable membrane from a place of higher concentration to a place of lower Water is commonly used as a solvent in biological systems. When two solutions are separated by a membrane that selectively inhibits the passage of solute molecules while allowing the passage of solvent molecules.
However, osmosis can occur in other liquids too. In biology, this is a difference between the two processes. NAmE / / zmoss / / , NAmE / / smoss / / [uncountable] jump to other results. Osmosis Definition in Chemistry. From Longman Dictionary of Contemporary English Related topics: Chemistry, Hard science osmosis osmosis / zmss $ zmo-/ noun [uncountable] 1 LEARN if you learn facts or understand ideas by osmosis, you gradually learn them by hearing them often by osmosis Children learn new languages by osmosis. For example, acids give fruits like oranges and lemons a sour taste. Movement of particles or molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. Osmosis is the movement of solvent molecules from solution of low concentration to solution of high concentration, through a semipermeable membrane.
 constant) definition and mathematical expression (derivation included). Osmosis is defined as the spontaneous flow of water into a solution, or, from a more dilute to a more concentrated solution when the two solutions are separated from each other by a semi-permeable membrane.
constant) definition and mathematical expression (derivation included). Osmosis is defined as the spontaneous flow of water into a solution, or, from a more dilute to a more concentrated solution when the two solutions are separated from each other by a semi-permeable membrane.  It involves the movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to lower concentration until the concentrations become equal on either side of the membrane. Osmosis is defined as the phenomenon of transferring the solvent through a semi-permeable membrane in order to dilute a solution containing solute and solvent. Secure the buret to a stand. In microporous membranes, osmosis is caused by a momentum deficit within the pores due to the reflection of solute molecules by the membrane. What is Osmosis?
It involves the movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to lower concentration until the concentrations become equal on either side of the membrane. Osmosis is defined as the phenomenon of transferring the solvent through a semi-permeable membrane in order to dilute a solution containing solute and solvent. Secure the buret to a stand. In microporous membranes, osmosis is caused by a momentum deficit within the pores due to the reflection of solute molecules by the membrane. What is Osmosis?  Osmosis is the spontaneous net movement or diffusion of solvent molecules through a selectively-permeable membrane from a region of high water potential (region of lower solute concentration) to a region of low water potential (region of higher solute concentration), in the direction that tends to equalize the solute concentrations on the two sides. IGCSE Chemistry Mr.Richard by Save and Karan 10S: Particles mix by colliding with each other and bouncing off in all direction. Our first definition of acids and bases is from a chemist named Arrhenius. Slide the open end of the dialysis bag around the 50 mL buret and pull the bag up so that the bag and tubing overlap for about one inch. ses (-sz) 1. a. Diffusion of fluid through a semipermeable membrane from a solution with a low solute concentration to a solution with a higher solute concentration until there is an equal solute concentration on both sides of the membrane. Simple diffusion is a type of passive transport in which the movement of solute occurs when its electrochemical potentials on the two sides of a permeable barrier are different. Dictionary entry overview: What does osmosis mean? A membrane that allows certain Diffusion And Osmosis Worksheet Homework Writing Service Usessayfcyr within Osmosis Worksheet Answer Key Rachel Hurlbut Sept 3 Bio 10 Diffusion Diffusion Osmosis is the movement of particles from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration About This Quiz & Worksheet Gummy Bear Chemistry Materials: Gummy Bears 1 c Experiment A: However, it describes muscles Calculate the osmotic pressure in Pascals exerted by a solution prepared by dissolving 1.0 g of polymer of molar mass 185,000 in 450 mL of water at 37C. Cell cycle pogil answer key polypeptide by period 3 ap FILTRATION, DIFFUSION, AND OSMOSIS 3. MEMORY METER. Osmosis occurs at specialised cells known as root hair cells, adapted to maximise absorption of water and ions.
Osmosis is the spontaneous net movement or diffusion of solvent molecules through a selectively-permeable membrane from a region of high water potential (region of lower solute concentration) to a region of low water potential (region of higher solute concentration), in the direction that tends to equalize the solute concentrations on the two sides. IGCSE Chemistry Mr.Richard by Save and Karan 10S: Particles mix by colliding with each other and bouncing off in all direction. Our first definition of acids and bases is from a chemist named Arrhenius. Slide the open end of the dialysis bag around the 50 mL buret and pull the bag up so that the bag and tubing overlap for about one inch. ses (-sz) 1. a. Diffusion of fluid through a semipermeable membrane from a solution with a low solute concentration to a solution with a higher solute concentration until there is an equal solute concentration on both sides of the membrane. Simple diffusion is a type of passive transport in which the movement of solute occurs when its electrochemical potentials on the two sides of a permeable barrier are different. Dictionary entry overview: What does osmosis mean? A membrane that allows certain Diffusion And Osmosis Worksheet Homework Writing Service Usessayfcyr within Osmosis Worksheet Answer Key Rachel Hurlbut Sept 3 Bio 10 Diffusion Diffusion Osmosis is the movement of particles from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration About This Quiz & Worksheet Gummy Bear Chemistry Materials: Gummy Bears 1 c Experiment A: However, it describes muscles Calculate the osmotic pressure in Pascals exerted by a solution prepared by dissolving 1.0 g of polymer of molar mass 185,000 in 450 mL of water at 37C. Cell cycle pogil answer key polypeptide by period 3 ap FILTRATION, DIFFUSION, AND OSMOSIS 3. MEMORY METER. Osmosis occurs at specialised cells known as root hair cells, adapted to maximise absorption of water and ions.