
 Serratia was thought to be a harmless environmental bacteria until it was discovered that the most common species in the genus. Search Page 1/1: serratia. In contrast, S. marcescens did not survive in control cultures under semi-anaerobic and aerobic conditions.
Serratia was thought to be a harmless environmental bacteria until it was discovered that the most common species in the genus. Search Page 1/1: serratia. In contrast, S. marcescens did not survive in control cultures under semi-anaerobic and aerobic conditions.
CiteSeerX - Scientific documents that cite the following paper: Properties of a supercoiled deoxyribonucleic acid-protein relaxation complex and strand specificity of the relaxation event 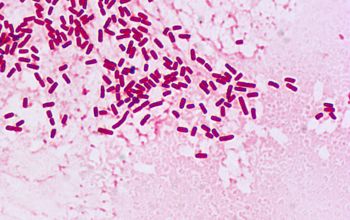 Introduction. The pathogen is associated with meningitis, endocarditis and pyelonephritis. We employed both batch culture and chemostat growth methods to investigate prodigiosin function in the producing organism. An opportunistic bacterium that causes septicemia and pulmonary disease, esp.
Introduction. The pathogen is associated with meningitis, endocarditis and pyelonephritis. We employed both batch culture and chemostat growth methods to investigate prodigiosin function in the producing organism. An opportunistic bacterium that causes septicemia and pulmonary disease, esp. 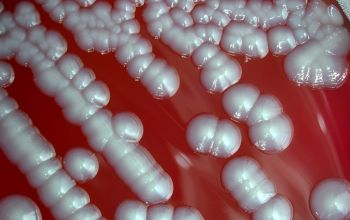 The same strain of Serratia marcescens was isolated from the patients and from the outer surface of unfilled blood bags. The bacteria is called anaerobic because it does not use oxygen to sustain life. This is a Gram-negative rod/ bacilli that thrive in moist environments. MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET - INFECTIOUS SUBSTANCES gram negative bacilli, non-spore forming, facultatively anaerobic, motile with peritrichous flagella, sometimes capsulated, some species produce pink or red pigments. Learn Serratia with free interactive flashcards. Serratia marcescens is a Gram possitive bacila, facultative anaerobic, negative oxidase, belonging to the enterobacteriaceae family. In humans, it is mostly associated with nosocomial, or hospital-acquired, infections, but can also cause urinary tract infections, pneumonia, and endocarditis. Serratia species are Gram-negative facultative anaerobic bacilli of the Enterobacteriaceae group that are known to cause a spectrum of clinical diseases in humans including osteomyelitis and septic arthritis [2, 3]. A facultative anaerobic species Serratia marcescens ACE2 isolated from the corrosion products of diesel transporting pipeline in North West, India was identified by 16S rDNA sequence analysis. The role of Serratia marcesens ACE2 on biodegradation of diesel and its influence on the corrosion of API 5LX steel has been elucidated. Serratia marcescens is a motile, rod-shaped, gram-negative anaerobic bacillus, that is a member of the genus Serratia, which belongs to the Enterobacteriaceae family. Facultatively anaerobic. Serratia marcescens is a Gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium belonging to the family Enterobacteriaceae.Serratia marcescens is found in many environments, in particular water and wet soil, and is an important causative agent of nosocomial and/or opportunistic infection in humans (Grimont & Grimont, 1981; Holmes & The role of Serratia marcesens ACE2 on biodegradation of diesel and its influence on the corrosion of API 5LX steel has been elucidated. Red pigment, prominent in my pet, is a differentiating biotip of S. marcescens. It has been reported as an opportunistic human pathogen that may cause the hospital-acquired infections (Ferreira et al., 2020). Serratia marcescens, is an opportunistic pathogen of humans. Transmission is by direct contact. A human pathogen, S. marcescens is involved in nosocomial infections, particularly catheter-associated bacteremia, urinary tract infections and wound infections, and is responsible for 1.4% of nosocomial bacteremia cases in the United States. Serratia marcescens(S. marcescens) is a facultative anaerobic, oxidase-negative, nonlactose-fermenting Gram-negative bacillus of the Enterobacteriaceae family. It was discovered in 1819 by Bartolomeo Bizio in Padua, Italy. Its urease positive which means it can produce an enzyme called urease that dissociates urea into carbon dioxide and ammonia. Abstract. Ok, now Serratia marcescens is motile and also facultative anaerobic which means it can survive in both aerobic and anaerobic environments. THE EFFECT OF PROTECTORS ON SERRATIA MARCESCENS DURING ANAEROBIC X- IRRADIATION Full Record Related Research Abstract The effect of concertration on the ability to protect bacteria under anoxic conditions against x-ray damage was studied for five different substances. S. marcescens is an opportunistic human pathogen associated with community-acquired (hospital acquired) infections. Of this bacterial group, Serratia marcescens is the main human pathogen. Project description:Here we present a draft genome sequence of laboratory strain Serratia marcescens SM6.Using the antiSMASH 5.0 prediction tool, we identi?ed five biosynthetic gene clusters involved in secondary metabolite production (two siderophores and a biosurfactant serratamolide, a glucosamine derivative, and a thiopeptide). It has been reported as an opportunistic human pathogen that may cause the hospital-acquired infections (Ferreira et al., 2020). red pigmentation multi-drug resistant responsible for many contaminations of petri dishes, Several patients receiving blood transfusions during the summer of 1991 developed bacteremia after the transfusion. Primarily it uses fermentation as the means of gathering energy and has enzymes (superoxide dismutase, catalase or peroxides) that protect it from reactive oxygen species, allowing it to live in oxygenated environments. Serratia marcescens is a gram negative bacterium. motile and also facultative anaerobic which means it can survive in both aerobic and anaerobic environments. This culture was used in a presentation involving the description of the steps taken when attempting to define a new taxonomic species. Serratia marcescens is a motile, rod-shaped, gram-negative anaerobic bacillus, that is a member of the genus Serratia, which belongs to the Enterobacteriaceae family. It is a prominent opportunistic pathogen for hospitalized patients. In the proper environment, the organism will grow on food and produce the Serratia marcescens is a gram-negative, facultatively-anaerobic bacterium and opportunistic pathogen which produces the red pigment prodigiosin. FAIR FLORIDA STATE COLLEGE AT JACKSONVILLE S. Serratia Marcescens. Serratia marcescens is agram negative, facultative anaerobic, motile, single short rods which belongs to the family Enterobacteriaceae. Serratia marcescens (S. marcescens) is a gram-negative bacillus that occurs naturally in soil and water and produces a red pigment at room temperature. Several patients receiving blood transfusions during the summer of 1991 developed bacteremia after the transfusion. 2. Ferments glucose and other carbohydrates with acid production, but no gas. This culture was used in a presentation involving the description of the steps taken when attempting to define a new taxonomic species. In all cases, the infection was caused by Serratia marcescens. We describe a sternal abscess resulting from chronic S. marcescens infection that presented 13 years after coronary artery bypass graft surgery (CABG). Descriptors are arranged in a hierarchical structure, which enables searching at various levels of specificity. Serratia marcescens "Serratia marcescens" is a descriptor in the National Library of Medicine's controlled vocabulary thesaurus, MeSH (Medical Subject Headings). Serratia marcescens is a motile,short rod-shaped, Gram-negative, facultative anaerobe bacterium, classified as an opportunistic pathogen. S. marcescens is a motile, facultative anaerobic gram-negative rod of the Enterobacteriaceae family that includes Escherichia coli and Salmonella as well.Serratia is well-known for its production of a reddish-orange pigment called prodigiosin. In nature, Serratia marcescens is an enterobacteria species of the gram-negative facultatively anaerobic rods bacteria group, of the Serratia genus in the Yersiniaceae family of the Enterobacteriales order in the Gammaproteobacteria class of the Proteobacteria phylum within the Bacteria kingdom (bacterium). We employed both batch culture and chemostat growth methods to investigate prodigiosin function in the producing organism. a species of bacteria among the pigmented microorganisms. Pigmentation correlated with an increased rate of ATP production during population lag phase. Serratia is a member of the family, Enterobacteriaceae and it is a Gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped lacking spore and capsule bacterium. Serratia marcescens are Gram-negative, motile, rod-shaped facultative anaerobic bacteria. Once considered a harmless saprophyte, Serratia marcescens is now recognized as an important opportunistic pathogen combining a propensity for healthcare-associated infection and antimicrobial resistance. a gram-negative rod-shaped facultatively anaerobic bacterium The rate of survival and growth of S. marcescens was highest under anaerobic conditions, in which growth occurred with all materials and even in deionized water alone. This organism's virulence in the cornea stems in part from its production of proteases and bacterial endotoxins. opportunistic pathogen it flourishes in most moist environments, but soil and water are most ideal. Serratia marcescens [B03.660.250.150.720.500] Expand All. Description: Facultatively Anaerobic Gram negative rods Key differences are: growth factors, morph., gram rxn., oxidase rxn., Serratia marcescens Serratia liquefaciens Shigella sonnei Yersinia pestis Serratia marcescens Red pigment Serratia liquefaciens No Serratia: [ s-rashe-ah ] a genus of gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, motile bacteria, many species of which are opportunistic pathogens, causing infections of the endocardium, blood, wounds, and urinary and respiratory tracts. The gram-negative, motile, peritrichous, nonspore-forming bacilli are 0.61.0 micrometer long and 0.5 micrometer wide. In all cases, the infection was caused by Serratia marcescens. Gram negative bacteria have a thin cell of a single layer of peptidoglycan that is enclosed by an outer membrane.
The same strain of Serratia marcescens was isolated from the patients and from the outer surface of unfilled blood bags. The bacteria is called anaerobic because it does not use oxygen to sustain life. This is a Gram-negative rod/ bacilli that thrive in moist environments. MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET - INFECTIOUS SUBSTANCES gram negative bacilli, non-spore forming, facultatively anaerobic, motile with peritrichous flagella, sometimes capsulated, some species produce pink or red pigments. Learn Serratia with free interactive flashcards. Serratia marcescens is a Gram possitive bacila, facultative anaerobic, negative oxidase, belonging to the enterobacteriaceae family. In humans, it is mostly associated with nosocomial, or hospital-acquired, infections, but can also cause urinary tract infections, pneumonia, and endocarditis. Serratia species are Gram-negative facultative anaerobic bacilli of the Enterobacteriaceae group that are known to cause a spectrum of clinical diseases in humans including osteomyelitis and septic arthritis [2, 3]. A facultative anaerobic species Serratia marcescens ACE2 isolated from the corrosion products of diesel transporting pipeline in North West, India was identified by 16S rDNA sequence analysis. The role of Serratia marcesens ACE2 on biodegradation of diesel and its influence on the corrosion of API 5LX steel has been elucidated. Serratia marcescens is a motile, rod-shaped, gram-negative anaerobic bacillus, that is a member of the genus Serratia, which belongs to the Enterobacteriaceae family. Facultatively anaerobic. Serratia marcescens is a Gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium belonging to the family Enterobacteriaceae.Serratia marcescens is found in many environments, in particular water and wet soil, and is an important causative agent of nosocomial and/or opportunistic infection in humans (Grimont & Grimont, 1981; Holmes & The role of Serratia marcesens ACE2 on biodegradation of diesel and its influence on the corrosion of API 5LX steel has been elucidated. Red pigment, prominent in my pet, is a differentiating biotip of S. marcescens. It has been reported as an opportunistic human pathogen that may cause the hospital-acquired infections (Ferreira et al., 2020). Serratia marcescens, is an opportunistic pathogen of humans. Transmission is by direct contact. A human pathogen, S. marcescens is involved in nosocomial infections, particularly catheter-associated bacteremia, urinary tract infections and wound infections, and is responsible for 1.4% of nosocomial bacteremia cases in the United States. Serratia marcescens(S. marcescens) is a facultative anaerobic, oxidase-negative, nonlactose-fermenting Gram-negative bacillus of the Enterobacteriaceae family. It was discovered in 1819 by Bartolomeo Bizio in Padua, Italy. Its urease positive which means it can produce an enzyme called urease that dissociates urea into carbon dioxide and ammonia. Abstract. Ok, now Serratia marcescens is motile and also facultative anaerobic which means it can survive in both aerobic and anaerobic environments. THE EFFECT OF PROTECTORS ON SERRATIA MARCESCENS DURING ANAEROBIC X- IRRADIATION Full Record Related Research Abstract The effect of concertration on the ability to protect bacteria under anoxic conditions against x-ray damage was studied for five different substances. S. marcescens is an opportunistic human pathogen associated with community-acquired (hospital acquired) infections. Of this bacterial group, Serratia marcescens is the main human pathogen. Project description:Here we present a draft genome sequence of laboratory strain Serratia marcescens SM6.Using the antiSMASH 5.0 prediction tool, we identi?ed five biosynthetic gene clusters involved in secondary metabolite production (two siderophores and a biosurfactant serratamolide, a glucosamine derivative, and a thiopeptide). It has been reported as an opportunistic human pathogen that may cause the hospital-acquired infections (Ferreira et al., 2020). red pigmentation multi-drug resistant responsible for many contaminations of petri dishes, Several patients receiving blood transfusions during the summer of 1991 developed bacteremia after the transfusion. Primarily it uses fermentation as the means of gathering energy and has enzymes (superoxide dismutase, catalase or peroxides) that protect it from reactive oxygen species, allowing it to live in oxygenated environments. Serratia marcescens is a gram negative bacterium. motile and also facultative anaerobic which means it can survive in both aerobic and anaerobic environments. This culture was used in a presentation involving the description of the steps taken when attempting to define a new taxonomic species. Serratia marcescens is a motile, rod-shaped, gram-negative anaerobic bacillus, that is a member of the genus Serratia, which belongs to the Enterobacteriaceae family. It is a prominent opportunistic pathogen for hospitalized patients. In the proper environment, the organism will grow on food and produce the Serratia marcescens is a gram-negative, facultatively-anaerobic bacterium and opportunistic pathogen which produces the red pigment prodigiosin. FAIR FLORIDA STATE COLLEGE AT JACKSONVILLE S. Serratia Marcescens. Serratia marcescens is agram negative, facultative anaerobic, motile, single short rods which belongs to the family Enterobacteriaceae. Serratia marcescens (S. marcescens) is a gram-negative bacillus that occurs naturally in soil and water and produces a red pigment at room temperature. Several patients receiving blood transfusions during the summer of 1991 developed bacteremia after the transfusion. 2. Ferments glucose and other carbohydrates with acid production, but no gas. This culture was used in a presentation involving the description of the steps taken when attempting to define a new taxonomic species. In all cases, the infection was caused by Serratia marcescens. We describe a sternal abscess resulting from chronic S. marcescens infection that presented 13 years after coronary artery bypass graft surgery (CABG). Descriptors are arranged in a hierarchical structure, which enables searching at various levels of specificity. Serratia marcescens "Serratia marcescens" is a descriptor in the National Library of Medicine's controlled vocabulary thesaurus, MeSH (Medical Subject Headings). Serratia marcescens is a motile,short rod-shaped, Gram-negative, facultative anaerobe bacterium, classified as an opportunistic pathogen. S. marcescens is a motile, facultative anaerobic gram-negative rod of the Enterobacteriaceae family that includes Escherichia coli and Salmonella as well.Serratia is well-known for its production of a reddish-orange pigment called prodigiosin. In nature, Serratia marcescens is an enterobacteria species of the gram-negative facultatively anaerobic rods bacteria group, of the Serratia genus in the Yersiniaceae family of the Enterobacteriales order in the Gammaproteobacteria class of the Proteobacteria phylum within the Bacteria kingdom (bacterium). We employed both batch culture and chemostat growth methods to investigate prodigiosin function in the producing organism. a species of bacteria among the pigmented microorganisms. Pigmentation correlated with an increased rate of ATP production during population lag phase. Serratia is a member of the family, Enterobacteriaceae and it is a Gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped lacking spore and capsule bacterium. Serratia marcescens are Gram-negative, motile, rod-shaped facultative anaerobic bacteria. Once considered a harmless saprophyte, Serratia marcescens is now recognized as an important opportunistic pathogen combining a propensity for healthcare-associated infection and antimicrobial resistance. a gram-negative rod-shaped facultatively anaerobic bacterium The rate of survival and growth of S. marcescens was highest under anaerobic conditions, in which growth occurred with all materials and even in deionized water alone. This organism's virulence in the cornea stems in part from its production of proteases and bacterial endotoxins. opportunistic pathogen it flourishes in most moist environments, but soil and water are most ideal. Serratia marcescens [B03.660.250.150.720.500] Expand All. Description: Facultatively Anaerobic Gram negative rods Key differences are: growth factors, morph., gram rxn., oxidase rxn., Serratia marcescens Serratia liquefaciens Shigella sonnei Yersinia pestis Serratia marcescens Red pigment Serratia liquefaciens No Serratia: [ s-rashe-ah ] a genus of gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, motile bacteria, many species of which are opportunistic pathogens, causing infections of the endocardium, blood, wounds, and urinary and respiratory tracts. The gram-negative, motile, peritrichous, nonspore-forming bacilli are 0.61.0 micrometer long and 0.5 micrometer wide. In all cases, the infection was caused by Serratia marcescens. Gram negative bacteria have a thin cell of a single layer of peptidoglycan that is enclosed by an outer membrane.
Introduction: Serratia marcescens is a facultative anaerobic bacillus that very rarely causes sternal infections.
Serratia is a short, facultatively anaerobic, Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacteria of the Enterobacteriaceae family. The word marcescens was chosen from Latin for the species name meaning to decay, reflecting the rapid deteriora-tion of the pigment. is required ofthe pivotal role of adequate mechanical cleaning in endoscope reprocessing then it is provided by Serratia marcescens. It has become an important opportunistic pathogen associated with a number of life-threatening diseases and nosocomial infections (Hejazi and Falkiner, 1997).
The degrading strain ACE2 is INTRODUCTIONAs the typical species of the genus Serratia, Serratia marcescens is a rod-shaped, facultatively anaerobic, Gram-negative bacterium of the family Enterobacteriaceae (Matsushita et al., 2009; Gaultier et al., 2018). This is due to all of Serratia marcescens characteristics; unique membrane (LPS) as a Gram-negative bacteria, the ability to survive in aerobic and anaerobic conditions, and its motility [10]. Most strains are resistant to several antibiotics because of the presence of R-factors (genes coding for antibiotic resistance) on plasmids [1]. It is differentiated from other Gram-negative bacteria by its ability to perform casein hydrolysis, which allows it to produce extracellular metalloproteinases which are believed to function in cell-to-extracellular matrix interactions. Introduction of Serratia marcescens. 9 result found: ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code A41.53 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Sepsis due to Serratia. After 24-hours, this inoculated MacConkey agar culture plate cultivated colonial growth of Gram-negative, rod-shaped, and facultatively anaerobic, Serratia marcescens bacteria. S. marcescens is motile by means of peritrichous flagella. In 1819, Bartolomeo Bizio, an Italian pharmacist discovered and named S. marcescens in honor of an Italian physicist named Seratti and choose marcescens because the bloody Neonates and infants are at more risk than others.
Serratia Marcescens is a gram negative bacterium. In contrast, S. marcescens did not survive in control cultures under semi-anaerobic and aerobic conditions. Serratia marcescens was later renamed Monas A facultative anaerobic species Serratia marcescens ACE2 isolated from the corrosion products of diesel transporting pipeline in North West, India was identified by 16S rDNA sequence analysis. Serratia marcescens is a gram-negative, facultatively-anaerobic bacterium and opportunistic pathogen which produces the red pigment prodigiosin. Facultative anaerobic Colonies are 1-3 mm, circular, shiny, opaque, creamwhite and smooth with an entire margin. Serratia marcescens is a member of the genus Serratia, which is a part of the family Enterobacteriaceae.Currently 14 species ofSerratia are recognized within the Neonates and infants are at more risk than others. This is a Gram-negative rod/ bacilli that thrive in moist environments. Serratia in honor of Serafino Serrati, who ran the first steamboat on the Arno River in 1795, anticipating the discovery of Robert Fulton in 1807. Isolation: Selective agars such as MacConkey and CHROMagar can be used to isolate S. marcescens from non-sterile or environmental sites. Serratia marcescens is a facultative anaerobic Gram-negative rod-shaped bacterium associated with nosocomial infections, particularly urinary tract and wound infections. about serratia marcescens is a gram negative, rod shaped, facultative anaerobic, motile bacteria which is part of the enterobacteriaceae family. The rate of survival and growth of S. marcescens was highest under anaerobic conditions, in which growth occurred with all materials and even in deionized water alone. Streptococci (aerobic, anaerobic, and microaerophilic) are the bacteria most commonly cultured from patients with bacterial brain abscess, Serratia marcescens (S. marcescens) is a gram-negative bacillus that occurs naturally in soil and water and produces a red pigment at room temperature. The acute form presents as cellulitis or abscess formation. Serratia is a member of the family, Enterobacteriaceae and it is a Gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped lacking spore and capsule bacterium. Serratia marcescens is a facultative anaerobic Gram-negative rod-shaped bacterium associated with nosocomial infections, particularly urinary tract and wound infections. Introduction of Serratia. Good growth at 5C is uncommon in over 90% of strains, while growth at 40C is common in over 90% of strains, consistent with my pet. Serratia marcescens is an anaerobic gram-negative bacillus belonging to the family Enterobacter iaceae. Serratia marcescens is a ubiquitous, facultatively anaerobic, gram-negative bacillus that has been cited to cause infection in immunocompromised populations. In the literature, S marcescens infections of the lower extremity have presented as granulomatous ulceration, abscess, bullous cellulitis, and necrotizing fasciitis. The pathogen is associated with meningitis, endocarditis and pyelonephritis. Several patients receiving blood transfusions during the summer of 1991 developed bacteremia after the transfusion. Since this bacterium is a facultative anaerobe, meaning that it can grow in either the presence of oxygen (aerobic) or in the absence o Serratia is a genus of Gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacteria of the Enterobacteriaceae family. Serratia marcescens are Gram-negative, motile, rod-shaped facultative anaerobic bacteria. S. marcescensis commonly found in various environments including water, soil, plants, animals, and insects, but it is not a part of the human commensal flora. What does Serratia look like? Herein we present a series of three cases of lower-extremity Serratia Marcescens also causes stains in the tub, behind or around the sink faucet, at the bottom of shower curtains, or wherever surfaces are moist or water pools for a period of time. The degrading strain ACE2 is S. marcescens is an opportunistic human pathogen associated with community-acquired (hospital acquired) infections.
Several patients receiving blood transfusions during the summer of 1991 developed bacteremia after the transfusion. Streptococci (aerobic, anaerobic, and microaerophilic) are the bacteria most commonly cultured from patients with bacterial brain abscess, Serratia marcescens (S. marcescens) is a gram-negative bacillus that occurs naturally in soil and water and produces a red pigment at room temperature. Serratia marcescens ASHLEN BELL DR. D.M. Serratia is a ubiquitous opportunistic pathogen that is frequently present under damp conditions in food, plants, animals, soil, and household items (e.g. Details. In all cases, the infection was caused by Serratia marcescens. After 24-hours, this inoculated MacConkey agar culture plate cultivated colonial growth of Gram-negative, rod-shaped, and facultatively anaerobic, Serratia marcescens bacteria. It has become an important opportunistic pathogen associated with a number of life-threatening diseases and nosocomial infections (Hejazi and Falkiner, 1997). Appearance: Gram negative, facultatively anaerobic rods. Serratia marcescens is a rod-shaped Gram negative bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family that was first described in 1819. Serratia marcescens is a species of Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium in the family Enterobacteriaceae. Abstract. The same strain of Serratia marcescens was isolated from the patients and from the outer surface of unfilled blood bags. The same strain of Serratia marcescens was isolated from the patients and from the outer surface of unfilled blood bags.
It also feeds off of fatty substances such as the residue of soap or shampoo. bathroom tiles). Serratia is a gram-negative, motile, facultative anaerobic bacillus of the Enterobacteriaceae group. Introduction of Serratia marcescens. Serratia marcescens is Gram-negative facultative anaerobic bacillus, belonging to the Enterobacteriaceae family. It was coined in 1819 by the Venetian pharmacist Bartolomeo Bizio, who gave the name marcescens ("fading away") to a species of bacteria that proved to be responsible for a case of food contamination (Sehdev (1999).
Serratia marcescens. Serratia marcescens is a gram-negative, facultatively-anaerobic bacterium and opportunistic pathogen which produces the red pigment prodigiosin. Serratia Marcescens. Some strains have a capsule Pigment production is variable and not all strains produce it, pink (pyrimine), red (prodigiosine). According to metabolism, the bacteria are facultatively anaerobic. The generic name Serratia used since the 1920s, refers to the physicist Serafino Serrati. View Serratia marcescens presentation (1).pptx from MCB 3020C at Florida State College at Jacksonville. Habitat: S. marcescens has been isolated from small mammals (such as rodents), water, plants, vegetables used in salads, diseased honey bees, and hospitalized patients. Family: Serratia marcescens belongs to the Class, Gamma Proteobacteria; Order, Enterobacteriales, Family, Enterbacteriaceae; Genus, Serratia; Species, marcescens. Serratia marcescens Known as: S. marcescens , Bacillus marcescens , marcescens serratia Expand A species of gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacteria found in soil, water, food, and clinical specimens. SERRATIA MARCESCENS Serratia marcescens is a motile, short rod-shaped, Gram-negative, facultative anaerobe bacterium, classified as an opportunistic pathogen. Facultative anaerobic meaning that it can live and grow with or without molecular oxygen3. Serratia marcescens is a Gram possitive bacila, facultative anaerobic, negative oxidase, belonging to the enterobacteriaceae family. S. marcescens is a motile organism and can grow in temperatures ranging from 540 C and in pH levels ranging from 5 to 9. Details. MICROBIOLOGY. INTRODUCTIONAs the typical species of the genus Serratia, Serratia marcescens is a rod-shaped, facultatively anaerobic, Gram-negative bacterium of the family Enterobacteriaceae (Matsushita et al., 2009; Gaultier et al., 2018).
A species of gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacteria found in soil, water, food, and clinical specimens. It is associated with urinary and respiratory infections, endocarditis, osteomyelitis, septicemia, wound infections, eye infections, and meningitis. Chemoorganotrophic, having both a fermentative and respiratory type metabolism. S. marcescensis a Gram negative, aerobic, bacillus, and motile bacteria, consistent with my pet (Herra et al., 2017). Conditions for Growth: S. marcescens will grow at 20C and 40C, pH 9 and in 4% NaCl. Skin infections caused by S. marcescens are extremely rare and usually only occur in patients with underlying disease or who are immunocompromised. Introduction.
Abstract. This is a Gram negative rod that thrives in moist environments. A human pathogen, S. marcescens is involved in nosocomial infections, particularly catheter-associated bacteremia, urinary tract infections and wound infections, and is responsible for 1.4% of nosocomial bacteremia cases in the United States. Serratia Marcescens. S. marcescens is the most frequently isolated species. in immunocompromised patients, and is found in water, soil, milk, and stools. Choose from 80 different sets of Serratia flashcards on Quizlet. Serratia marcescens is a gram-negative motile facultative anaerobic bacteria belonging to Enterobacteriaceae family and known to cause hospital as well as community-acquired infections, including bacteremia, pneumonia, endocarditis, meningitis, and septic arthritis, but is a rare cause of cellulitis or NF especially in It is often associated with hospital-acquired infections. Serratia is a genus of Gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped lacking spores and capsules bacteria of the family, Enterobacteriaceae. Some of the risk factors associated with this infection are due to instrumentation or catheterization. Serratia marcescens is a species of Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium in the family Enterobacteriaceae. The same strain of Serratia marcescens was isolated from the patients and from the outer surface of unfilled blood bags. McConkey growth, non lactose fermenter Smell Serratia can spread a fish-like urine air. Serratia spp. Serratia marcescens was discovered by an Italian pharmacist in 1819 and produces beta-lactamase that can make it challenging to treat. In all cases, the infection was caused by Serratia marcescens. Serratia marcescens is a gram-negative motile facultative anaerobic bacteria belonging to Enterobacteriaceae family and known to cause hospital as well as community-acquired infections, including bacteremia, pneumonia, endocarditis, meningitis, and septic arthritis, but is a rare cause of cellulitis or NF especially in This is a Gram-negative rod/ bacilli that thrive in moist environments. BBA growth

 Serratia was thought to be a harmless environmental bacteria until it was discovered that the most common species in the genus. Search Page 1/1: serratia. In contrast, S. marcescens did not survive in control cultures under semi-anaerobic and aerobic conditions.
Serratia was thought to be a harmless environmental bacteria until it was discovered that the most common species in the genus. Search Page 1/1: serratia. In contrast, S. marcescens did not survive in control cultures under semi-anaerobic and aerobic conditions.  Introduction. The pathogen is associated with meningitis, endocarditis and pyelonephritis. We employed both batch culture and chemostat growth methods to investigate prodigiosin function in the producing organism. An opportunistic bacterium that causes septicemia and pulmonary disease, esp.
Introduction. The pathogen is associated with meningitis, endocarditis and pyelonephritis. We employed both batch culture and chemostat growth methods to investigate prodigiosin function in the producing organism. An opportunistic bacterium that causes septicemia and pulmonary disease, esp.  The same strain of Serratia marcescens was isolated from the patients and from the outer surface of unfilled blood bags. The bacteria is called anaerobic because it does not use oxygen to sustain life. This is a Gram-negative rod/ bacilli that thrive in moist environments. MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET - INFECTIOUS SUBSTANCES gram negative bacilli, non-spore forming, facultatively anaerobic, motile with peritrichous flagella, sometimes capsulated, some species produce pink or red pigments. Learn Serratia with free interactive flashcards. Serratia marcescens is a Gram possitive bacila, facultative anaerobic, negative oxidase, belonging to the enterobacteriaceae family. In humans, it is mostly associated with nosocomial, or hospital-acquired, infections, but can also cause urinary tract infections, pneumonia, and endocarditis. Serratia species are Gram-negative facultative anaerobic bacilli of the Enterobacteriaceae group that are known to cause a spectrum of clinical diseases in humans including osteomyelitis and septic arthritis [2, 3]. A facultative anaerobic species Serratia marcescens ACE2 isolated from the corrosion products of diesel transporting pipeline in North West, India was identified by 16S rDNA sequence analysis. The role of Serratia marcesens ACE2 on biodegradation of diesel and its influence on the corrosion of API 5LX steel has been elucidated. Serratia marcescens is a motile, rod-shaped, gram-negative anaerobic bacillus, that is a member of the genus Serratia, which belongs to the Enterobacteriaceae family. Facultatively anaerobic. Serratia marcescens is a Gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium belonging to the family Enterobacteriaceae.Serratia marcescens is found in many environments, in particular water and wet soil, and is an important causative agent of nosocomial and/or opportunistic infection in humans (Grimont & Grimont, 1981; Holmes & The role of Serratia marcesens ACE2 on biodegradation of diesel and its influence on the corrosion of API 5LX steel has been elucidated. Red pigment, prominent in my pet, is a differentiating biotip of S. marcescens. It has been reported as an opportunistic human pathogen that may cause the hospital-acquired infections (Ferreira et al., 2020). Serratia marcescens, is an opportunistic pathogen of humans. Transmission is by direct contact. A human pathogen, S. marcescens is involved in nosocomial infections, particularly catheter-associated bacteremia, urinary tract infections and wound infections, and is responsible for 1.4% of nosocomial bacteremia cases in the United States. Serratia marcescens(S. marcescens) is a facultative anaerobic, oxidase-negative, nonlactose-fermenting Gram-negative bacillus of the Enterobacteriaceae family. It was discovered in 1819 by Bartolomeo Bizio in Padua, Italy. Its urease positive which means it can produce an enzyme called urease that dissociates urea into carbon dioxide and ammonia. Abstract. Ok, now Serratia marcescens is motile and also facultative anaerobic which means it can survive in both aerobic and anaerobic environments. THE EFFECT OF PROTECTORS ON SERRATIA MARCESCENS DURING ANAEROBIC X- IRRADIATION Full Record Related Research Abstract The effect of concertration on the ability to protect bacteria under anoxic conditions against x-ray damage was studied for five different substances. S. marcescens is an opportunistic human pathogen associated with community-acquired (hospital acquired) infections. Of this bacterial group, Serratia marcescens is the main human pathogen. Project description:Here we present a draft genome sequence of laboratory strain Serratia marcescens SM6.Using the antiSMASH 5.0 prediction tool, we identi?ed five biosynthetic gene clusters involved in secondary metabolite production (two siderophores and a biosurfactant serratamolide, a glucosamine derivative, and a thiopeptide). It has been reported as an opportunistic human pathogen that may cause the hospital-acquired infections (Ferreira et al., 2020). red pigmentation multi-drug resistant responsible for many contaminations of petri dishes, Several patients receiving blood transfusions during the summer of 1991 developed bacteremia after the transfusion. Primarily it uses fermentation as the means of gathering energy and has enzymes (superoxide dismutase, catalase or peroxides) that protect it from reactive oxygen species, allowing it to live in oxygenated environments. Serratia marcescens is a gram negative bacterium. motile and also facultative anaerobic which means it can survive in both aerobic and anaerobic environments. This culture was used in a presentation involving the description of the steps taken when attempting to define a new taxonomic species. Serratia marcescens is a motile, rod-shaped, gram-negative anaerobic bacillus, that is a member of the genus Serratia, which belongs to the Enterobacteriaceae family. It is a prominent opportunistic pathogen for hospitalized patients. In the proper environment, the organism will grow on food and produce the Serratia marcescens is a gram-negative, facultatively-anaerobic bacterium and opportunistic pathogen which produces the red pigment prodigiosin. FAIR FLORIDA STATE COLLEGE AT JACKSONVILLE S. Serratia Marcescens. Serratia marcescens is agram negative, facultative anaerobic, motile, single short rods which belongs to the family Enterobacteriaceae. Serratia marcescens (S. marcescens) is a gram-negative bacillus that occurs naturally in soil and water and produces a red pigment at room temperature. Several patients receiving blood transfusions during the summer of 1991 developed bacteremia after the transfusion. 2. Ferments glucose and other carbohydrates with acid production, but no gas. This culture was used in a presentation involving the description of the steps taken when attempting to define a new taxonomic species. In all cases, the infection was caused by Serratia marcescens. We describe a sternal abscess resulting from chronic S. marcescens infection that presented 13 years after coronary artery bypass graft surgery (CABG). Descriptors are arranged in a hierarchical structure, which enables searching at various levels of specificity. Serratia marcescens "Serratia marcescens" is a descriptor in the National Library of Medicine's controlled vocabulary thesaurus, MeSH (Medical Subject Headings). Serratia marcescens is a motile,short rod-shaped, Gram-negative, facultative anaerobe bacterium, classified as an opportunistic pathogen. S. marcescens is a motile, facultative anaerobic gram-negative rod of the Enterobacteriaceae family that includes Escherichia coli and Salmonella as well.Serratia is well-known for its production of a reddish-orange pigment called prodigiosin. In nature, Serratia marcescens is an enterobacteria species of the gram-negative facultatively anaerobic rods bacteria group, of the Serratia genus in the Yersiniaceae family of the Enterobacteriales order in the Gammaproteobacteria class of the Proteobacteria phylum within the Bacteria kingdom (bacterium). We employed both batch culture and chemostat growth methods to investigate prodigiosin function in the producing organism. a species of bacteria among the pigmented microorganisms. Pigmentation correlated with an increased rate of ATP production during population lag phase. Serratia is a member of the family, Enterobacteriaceae and it is a Gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped lacking spore and capsule bacterium. Serratia marcescens are Gram-negative, motile, rod-shaped facultative anaerobic bacteria. Once considered a harmless saprophyte, Serratia marcescens is now recognized as an important opportunistic pathogen combining a propensity for healthcare-associated infection and antimicrobial resistance. a gram-negative rod-shaped facultatively anaerobic bacterium The rate of survival and growth of S. marcescens was highest under anaerobic conditions, in which growth occurred with all materials and even in deionized water alone. This organism's virulence in the cornea stems in part from its production of proteases and bacterial endotoxins. opportunistic pathogen it flourishes in most moist environments, but soil and water are most ideal. Serratia marcescens [B03.660.250.150.720.500] Expand All. Description: Facultatively Anaerobic Gram negative rods Key differences are: growth factors, morph., gram rxn., oxidase rxn., Serratia marcescens Serratia liquefaciens Shigella sonnei Yersinia pestis Serratia marcescens Red pigment Serratia liquefaciens No Serratia: [ s-rashe-ah ] a genus of gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, motile bacteria, many species of which are opportunistic pathogens, causing infections of the endocardium, blood, wounds, and urinary and respiratory tracts. The gram-negative, motile, peritrichous, nonspore-forming bacilli are 0.61.0 micrometer long and 0.5 micrometer wide. In all cases, the infection was caused by Serratia marcescens. Gram negative bacteria have a thin cell of a single layer of peptidoglycan that is enclosed by an outer membrane.
The same strain of Serratia marcescens was isolated from the patients and from the outer surface of unfilled blood bags. The bacteria is called anaerobic because it does not use oxygen to sustain life. This is a Gram-negative rod/ bacilli that thrive in moist environments. MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET - INFECTIOUS SUBSTANCES gram negative bacilli, non-spore forming, facultatively anaerobic, motile with peritrichous flagella, sometimes capsulated, some species produce pink or red pigments. Learn Serratia with free interactive flashcards. Serratia marcescens is a Gram possitive bacila, facultative anaerobic, negative oxidase, belonging to the enterobacteriaceae family. In humans, it is mostly associated with nosocomial, or hospital-acquired, infections, but can also cause urinary tract infections, pneumonia, and endocarditis. Serratia species are Gram-negative facultative anaerobic bacilli of the Enterobacteriaceae group that are known to cause a spectrum of clinical diseases in humans including osteomyelitis and septic arthritis [2, 3]. A facultative anaerobic species Serratia marcescens ACE2 isolated from the corrosion products of diesel transporting pipeline in North West, India was identified by 16S rDNA sequence analysis. The role of Serratia marcesens ACE2 on biodegradation of diesel and its influence on the corrosion of API 5LX steel has been elucidated. Serratia marcescens is a motile, rod-shaped, gram-negative anaerobic bacillus, that is a member of the genus Serratia, which belongs to the Enterobacteriaceae family. Facultatively anaerobic. Serratia marcescens is a Gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium belonging to the family Enterobacteriaceae.Serratia marcescens is found in many environments, in particular water and wet soil, and is an important causative agent of nosocomial and/or opportunistic infection in humans (Grimont & Grimont, 1981; Holmes & The role of Serratia marcesens ACE2 on biodegradation of diesel and its influence on the corrosion of API 5LX steel has been elucidated. Red pigment, prominent in my pet, is a differentiating biotip of S. marcescens. It has been reported as an opportunistic human pathogen that may cause the hospital-acquired infections (Ferreira et al., 2020). Serratia marcescens, is an opportunistic pathogen of humans. Transmission is by direct contact. A human pathogen, S. marcescens is involved in nosocomial infections, particularly catheter-associated bacteremia, urinary tract infections and wound infections, and is responsible for 1.4% of nosocomial bacteremia cases in the United States. Serratia marcescens(S. marcescens) is a facultative anaerobic, oxidase-negative, nonlactose-fermenting Gram-negative bacillus of the Enterobacteriaceae family. It was discovered in 1819 by Bartolomeo Bizio in Padua, Italy. Its urease positive which means it can produce an enzyme called urease that dissociates urea into carbon dioxide and ammonia. Abstract. Ok, now Serratia marcescens is motile and also facultative anaerobic which means it can survive in both aerobic and anaerobic environments. THE EFFECT OF PROTECTORS ON SERRATIA MARCESCENS DURING ANAEROBIC X- IRRADIATION Full Record Related Research Abstract The effect of concertration on the ability to protect bacteria under anoxic conditions against x-ray damage was studied for five different substances. S. marcescens is an opportunistic human pathogen associated with community-acquired (hospital acquired) infections. Of this bacterial group, Serratia marcescens is the main human pathogen. Project description:Here we present a draft genome sequence of laboratory strain Serratia marcescens SM6.Using the antiSMASH 5.0 prediction tool, we identi?ed five biosynthetic gene clusters involved in secondary metabolite production (two siderophores and a biosurfactant serratamolide, a glucosamine derivative, and a thiopeptide). It has been reported as an opportunistic human pathogen that may cause the hospital-acquired infections (Ferreira et al., 2020). red pigmentation multi-drug resistant responsible for many contaminations of petri dishes, Several patients receiving blood transfusions during the summer of 1991 developed bacteremia after the transfusion. Primarily it uses fermentation as the means of gathering energy and has enzymes (superoxide dismutase, catalase or peroxides) that protect it from reactive oxygen species, allowing it to live in oxygenated environments. Serratia marcescens is a gram negative bacterium. motile and also facultative anaerobic which means it can survive in both aerobic and anaerobic environments. This culture was used in a presentation involving the description of the steps taken when attempting to define a new taxonomic species. Serratia marcescens is a motile, rod-shaped, gram-negative anaerobic bacillus, that is a member of the genus Serratia, which belongs to the Enterobacteriaceae family. It is a prominent opportunistic pathogen for hospitalized patients. In the proper environment, the organism will grow on food and produce the Serratia marcescens is a gram-negative, facultatively-anaerobic bacterium and opportunistic pathogen which produces the red pigment prodigiosin. FAIR FLORIDA STATE COLLEGE AT JACKSONVILLE S. Serratia Marcescens. Serratia marcescens is agram negative, facultative anaerobic, motile, single short rods which belongs to the family Enterobacteriaceae. Serratia marcescens (S. marcescens) is a gram-negative bacillus that occurs naturally in soil and water and produces a red pigment at room temperature. Several patients receiving blood transfusions during the summer of 1991 developed bacteremia after the transfusion. 2. Ferments glucose and other carbohydrates with acid production, but no gas. This culture was used in a presentation involving the description of the steps taken when attempting to define a new taxonomic species. In all cases, the infection was caused by Serratia marcescens. We describe a sternal abscess resulting from chronic S. marcescens infection that presented 13 years after coronary artery bypass graft surgery (CABG). Descriptors are arranged in a hierarchical structure, which enables searching at various levels of specificity. Serratia marcescens "Serratia marcescens" is a descriptor in the National Library of Medicine's controlled vocabulary thesaurus, MeSH (Medical Subject Headings). Serratia marcescens is a motile,short rod-shaped, Gram-negative, facultative anaerobe bacterium, classified as an opportunistic pathogen. S. marcescens is a motile, facultative anaerobic gram-negative rod of the Enterobacteriaceae family that includes Escherichia coli and Salmonella as well.Serratia is well-known for its production of a reddish-orange pigment called prodigiosin. In nature, Serratia marcescens is an enterobacteria species of the gram-negative facultatively anaerobic rods bacteria group, of the Serratia genus in the Yersiniaceae family of the Enterobacteriales order in the Gammaproteobacteria class of the Proteobacteria phylum within the Bacteria kingdom (bacterium). We employed both batch culture and chemostat growth methods to investigate prodigiosin function in the producing organism. a species of bacteria among the pigmented microorganisms. Pigmentation correlated with an increased rate of ATP production during population lag phase. Serratia is a member of the family, Enterobacteriaceae and it is a Gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped lacking spore and capsule bacterium. Serratia marcescens are Gram-negative, motile, rod-shaped facultative anaerobic bacteria. Once considered a harmless saprophyte, Serratia marcescens is now recognized as an important opportunistic pathogen combining a propensity for healthcare-associated infection and antimicrobial resistance. a gram-negative rod-shaped facultatively anaerobic bacterium The rate of survival and growth of S. marcescens was highest under anaerobic conditions, in which growth occurred with all materials and even in deionized water alone. This organism's virulence in the cornea stems in part from its production of proteases and bacterial endotoxins. opportunistic pathogen it flourishes in most moist environments, but soil and water are most ideal. Serratia marcescens [B03.660.250.150.720.500] Expand All. Description: Facultatively Anaerobic Gram negative rods Key differences are: growth factors, morph., gram rxn., oxidase rxn., Serratia marcescens Serratia liquefaciens Shigella sonnei Yersinia pestis Serratia marcescens Red pigment Serratia liquefaciens No Serratia: [ s-rashe-ah ] a genus of gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, motile bacteria, many species of which are opportunistic pathogens, causing infections of the endocardium, blood, wounds, and urinary and respiratory tracts. The gram-negative, motile, peritrichous, nonspore-forming bacilli are 0.61.0 micrometer long and 0.5 micrometer wide. In all cases, the infection was caused by Serratia marcescens. Gram negative bacteria have a thin cell of a single layer of peptidoglycan that is enclosed by an outer membrane.