. Many of the studies examining sodium modelling did not control adequately for the concentration of sodium in the standard dialysate. The most serious side effects induced by related side effects are uncommon in peritoneal dialysis, hemodialysis therapy are caused by changes in sodium concen-where sodium and water exchanges are almost continu-tration and subsequent water shift between the intracellular ous. This will complicate the model by increasing the number of parameters and Without change in dry weight, post-dialysis SBPs declined from 174 to 118 mmHg with these interventions [ 26 ].  Method: The mini peritoneal equilibration test (mini- Abstract: Sodium volume modeling during hemodialysis encounters several difficulties. Sodium modeling. Sodium modeling in hemodiafiltration. Sodium concentration at point T1 was significantly increased during the sodium and the sodium + UF profile as compared with the control ( P < 0.05) ( Table 2). Detailed Description: Recent evidence from our group shows that individualization of the sodium concentration in the dialysate to match the patient's own serum sodium results in less thirst, less interdialytic weight gain, less HD-related symptoms, and better blood pressure control in hypertensive subjects.
Method: The mini peritoneal equilibration test (mini- Abstract: Sodium volume modeling during hemodialysis encounters several difficulties. Sodium modeling. Sodium modeling in hemodiafiltration. Sodium concentration at point T1 was significantly increased during the sodium and the sodium + UF profile as compared with the control ( P < 0.05) ( Table 2). Detailed Description: Recent evidence from our group shows that individualization of the sodium concentration in the dialysate to match the patient's own serum sodium results in less thirst, less interdialytic weight gain, less HD-related symptoms, and better blood pressure control in hypertensive subjects.  And there are many different causes, such as changes in kidney function, blood pressure medicines, or conditions like heart or liver failure.
And there are many different causes, such as changes in kidney function, blood pressure medicines, or conditions like heart or liver failure.
Thus, a twopool model must be considered.
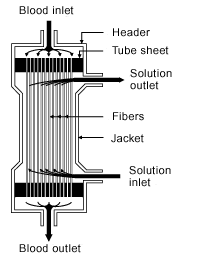 A locked padlock) or https:// means youve safely connected to the .gov website. A computer model was developed to simulate sodium and water kinetics during hemodiafiltration (HDF), acetate-free biofiltration (AFB) and hemodialysis (HD). Since the body attempts to maintain the sodium setpoint, even if water is removed during dialysis, these patients will drink more water during interdialytic period causing excess weight gain, increased ECF volumes and thus, higher blood pressures.13 During each block, one of three sodium programs or a constant (control) dialysate sodium of 138 mEq/L was used.
A locked padlock) or https:// means youve safely connected to the .gov website. A computer model was developed to simulate sodium and water kinetics during hemodiafiltration (HDF), acetate-free biofiltration (AFB) and hemodialysis (HD). Since the body attempts to maintain the sodium setpoint, even if water is removed during dialysis, these patients will drink more water during interdialytic period causing excess weight gain, increased ECF volumes and thus, higher blood pressures.13 During each block, one of three sodium programs or a constant (control) dialysate sodium of 138 mEq/L was used.  Abstract: Sodium volume modeling during hemodialysis encounters several difficulties. It is also used in conjunction with UF goals greater than 5 liters.
Abstract: Sodium volume modeling during hemodialysis encounters several difficulties. It is also used in conjunction with UF goals greater than 5 liters.
Sodium modeling is a helpful tool for the illustration of the effects of changes in sodium concentration and ultrafiltration rate on sodium balance during one dialysis session. Sodium modeling is a helpful tool for the illustration of the effects of changes in sodium concentration and ultrafiltration rate on sodium balance during one dialysis session. This study presented a numerical simulation model for estimating cardiovascular response in dialysis patients during sodium-profiled hemodialysis.
La Biblioteca Virtual en Salud es una coleccin de fuentes de informacin cientfica y tcnica en salud organizada y almacenada en formato electrnico en la Regin de Amrica Latina y el Caribe, accesible de forma universal en Internet de modo compatible con las bases internacionales. Sodium modelling is the method of altering sodium during the hemodialysis therapy so as to maintain the osmotic gradient in the blood for preventing hypotension especially. Sodium modeling dramatically decreases both intradialytic and interdialytic morbidity in young hemodialysis patients. In many dialysis patients, dry In sodium profiling, the sodium concentration in the dialysis fluid, instead of being constant, follows a time-dependent profile over the course of a hemodialysis session. A rise in body core temperature and loss of body water via sweating are natural consequences of prolonged exercise in the heat. Sodium modeling is a helpful tool for the illustration of the effects of changes in sodium concentration and ultrafiltration rate on sodium balance during one dialysis session. Intermittent hemodialysis remains a cornerstone of extracorporeal KRT in the intensive care unit, either as a first-line therapy for AKI or a second-line therapy when patients transition from a continuous or prolonged intermittent therapy.
Dialysate sodium concentration must be prescribed for each dialysis session. Dialysate sodium standards vary from 126.5mEq/L to gr eater than 155mEq/L through out the history of dialysis. 418-422. Hemodialysis patients at risk for, or predisposed to, IDH may benefit from lowering dialysate temperature, dialysate sodium modeling, and maintaining dialysate calcium at 3 mEq/L. Artif.
Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites. IDH-mitigating interventions for end-stage renal disease patients include cool dialysate, 6 albumin administration, 7 sequential ultrafiltration (UF)-HD, 8 and sodium modeling. First, the actual sodium distribution volume is the extracellular water, whereas the ultrafiltration flow reflects the variation of total body water. The main aim of this manipulation is to avoid osmotic disequilibrium by keeping plasma osmolality in the physiological range. Parsons et al . A report of five hemodialysis patients examined the effect of 68 g daily dietary salt restriction (2.43.2 g or 106140 mmol) in combination with a reduction in dialysate sodium from 142 to 135 mmol/L. Sodium ramping has been introduced as a technique to decrease side effects occurring during hemodialysis. Amia automated peritoneal dialysis (APD) with the Sharesource remote patient monitoring platform is the first and only APD system to include user-friendly features that help guide end-stage renal disease patients through home peritoneal dialysis (PD) therapy, while keeping them remotely connected. We studied sodium ramping in 414 dialysis sessions in 23 patients by randomizing 2-week blocks of dialysis to either steady dialysate sodium of 140 mEq/L, linear sodium ramping during dialysis from 155 mEq/L to 140 mEq/ L, or stepwise ramping Reducing dietary sodium intake remains the most important tool in improving blood control in dialysis patients by means of online measurements of plasma conductivity and adjustment of dialysate conductivity by feedback technologies. Multiple regression analysis of the results of 3,240 simulated applications of the model (1,620 HDF, 1,080 AFB, 540 HD) showed that, during HDF and AFB, there is a close
1 linear 2 step down 3 exponential 4 step down exponential The pur-pose of this review was to identify whether sodium profiling is an effective intervention in removing or reducing these untoward effects. Our units policy is there must be an order for anything less than 36 degrees. A new set of the same parameters was estimated for the Expanded model as for the Baseline model, using the same procedure. First, the actual sodium distribution volume is the extracellular water, whereas the ultrafiltration flow reflects the variation of total body water. Hypernatremia is thus a potential, but by all accounts, rare complication of tri-sodium citrate anticoagulation. As an alternative to sodium modeling and, as further reviewed below, some clinicians now individualize the dialysate sodium concentration by aligning dialysate sodium prescriptions with patient pre-dialysis serum sodium levels. Slide 1 What is sodium modeling in hemodialysis patients? It is necessary to add ascorbic acid in a quantity sufficiently to achieve at least a concentration of 1 Although the anuria persisted for a while, the increased amount of peritoneal dialysate easily normalized the acidemia and serum potassium level and is the perfect alternative for large-volume One may face increased utility costs com, Sodium profiling with a high dialysate sodium concentration is an effective method for the prevention of intra-dialytic hypotension, but also has possible drawbacks such as increased thirst, inter-dialytic weight gain and hypertension [1, 2].Recently, it has become possible to model the decline in blood volume and changes in plasma conductivity (PC), as a Bench dilute acid is usually of this.
Thus, a twopool model must be considered. haemodialysis involves diverting blood into an external machine, where it's filtered before being returned to the body.
Causes of Intradialytic hypotension(IDH) Intradialytic Hypotension Reduced ECV
Dialysate is an artiicial luid which reconstitutes ECF Sodium modeling programs are available on dialysis by removal of urea and other waste products and transfer of machines and allow alteration of sodium concentration over electrolytes and The dialysate sodium dip and estimation of siev-ing coefficient for sodium may be used for quantification of the free water fraction in ultrafiltration flow from blood to the peritoneal cavity. The dialysate sodium dip and estimation of siev-ing coefficient for sodium may be used for quantification of the free water fraction in ultrafiltration flow from blood to the peritoneal cavity. Water follows salt and if you increase the serum sodium it attracts water into the blood stream. By default, all patients at our dialysis center are started on HD with sodium modeling. Fluid overload in patients undergoing hemodialysis contributes to cardiovascular morbidity and is a major cause of hospitalizations. sodium concentrations, time varying (usually decreasing) dialysate sodium concentrations have been used in an approach called sodium modeling. As a general rule, hemodialysis patients have stable predialysis plasma sodium concentrations, and each patient has a fixed osmolar set point. Hypertonic dialysate sodium prescriptions, including sodium modeling, predispose to positive sodium balance and lead to higher blood pressure and increased interdialytic weight gain. In normal individuals, the tonicity exerted by dissolved sodium chloride determines plasma osmolality and indirectly determines intracellular tonicity and cell volume. Sodium chloride is the most abundant salt in extracellular fluid. There was no increase in adverse events associated with sodium modeling. Method: The mini peritoneal equilibration test (mini- 2. It's generally classified into four types. This approach was widely Side effects include increased interdialytic weight gain. Sodium profiling is a method employed to avoid unwanted side effects of hemodialysis therapy by deliberately changing the sodium concentration in dialysis fluid during the course of a dialysis The formula for sodium thiosulfate is Na 2 S 2 O 3 . 4 attempted to address this issue by comparing the responses of 12 patients to 4 different dialysis regimens, which included modelled sodium and ultrafiltration (UF), each over a 3 week period. The main aim of this manipulation is to avoid osmotic disequilibrium by keeping plasma osmolality in the physiological range. Multiple Abstract: Dialysate sodium (Na+) modeling in hemodialysis requires precise individual adjustment and control of Na+ dialysate concentration. By the early 1990s, Acchiardo advocated, [s]odium modelling [149mEq/L dropping to 140 mEq/L] should always be used in patients being maintained on high flux di alysis (Acchiardo & Hayden, 1991) . n,-n /) is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.. Many modern dialysis machines offer options for ultrafiltration (UFP) and sodium profiling (or sodium variation system [SVS]). Acute adverse side-effects of hemodialysis such as hypotension, muscle cramps, osmotic imbalance and thirst are induced by the interference with The relationship between serum and dialysate sodium and mortality appears to be variable. Clinical validation of the model was obtained in 12 patients: predicted final [Na+P] agreed well with the values measured by means of direct potentiometry and fully acceptable for clinical purposes. The main aim of this manipulation is to avoid osmotic disequilibrium by keeping plasma osmolality in the physiological range. Sodium Modeling. Further advantages of sodium profiling are a reduction in the incidence of muscle Sodium restriction is recommended if blood pressure is high or if you are retaining fluid. Sodium volume modeling during hemodialysis encounters several difficulties. It is often addressed by reinforcing the importance of a low-salt diet with patients and challenging estimated dry weights. Phase 1. Myositis disease activity is stable* 8. Sodium variation or modeling is a way to control hypotension, cramps and disequilibrium syndrome. We hypothesized that a sodium dialysate prescription resulting in a higher sodium gradient is associated with increases in interdialytic weight gain (IDWG), blood pressure (BP) and thirst. Water and sodium overload is the predominant factor in the pathogenesis of hypertension in dialysis patients. As cardiovascular stability and the delivery of the prescribed dialysis dose seem to be the main factors in determining the morbidity and mortality of hemodialyzer patients today, it Sodium is an electrolyte that balances the amount of fluid in the body, helps muscles and nerves work, and regulates blood pressure.
Those presets you mentioned are exactly what sodium variation is. Sodium modeling during hemodialysis: a new approach. A while back my company did a lot of sodium modeling as a means to keep BPs up during the runs. To counteract these effects, dialysate sodium concentration is increased by either fixing dialysate sodium at a higher concentration for the entire HD session or systematically varying the dialysate sodium concentration over the course of the HD session, a process called sodium modeling. Sodium profiling is a method employed to avoid unwanted side effects of hemodialysis therapy by deliberately changing the sodium concentration in dialysis fluid during the course of a The term for low sodium levels in the blood is hyponatremia. Sodium modeling is a helpful tool for the illustration of the effects of changes in sodium concentration and ultrafiltration rate on sodium balance during one dialysis session. It seems to me there are "fads" in dialysis and that sodium modeling is one of them.
In practice, the use of hyponatremic dialysis/replacement fluids usually compensates for addition of tri-sodium citrate. 7. Variations relate mainly to the low accuracy of dialysate concentrate (2.5% for Na+ is tolerated by the mEq/L (Barr, 1988). Eligibility: Can have IV access established to receive study infusions . There are 2 main types of dialysis : haemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis .
Introduction: Hemodialysis is the most common method - used to remove waste and toxic substances from the body, hence it is used to treat patients of different types of renal failure. Abstract: Dialysate sodium (Na+) modeling in hemodialysis requires precise individual adjustment and control of Na+ dialysate concentration. By means of this method the dialysate sodium concentration and the ultrafi Sodium modelling to reduce intradialytic hypotension during haemodialysis for acute kidney injury in the intensive care unit - Lynch - 2016 - Nephrology - Wiley Online Library Sodium modeling is a helpful tool for the illustration of the effects of changes in sodium concentration and ultrafiltration rate on sodium balance during one dialysis session. Dialysate sodium (Na+) modeling in hemodialysis requires precise individual adjustment and control of Na+ dialysate concentration. The effects of sodium modeling were evaluated in 16 adolescent and young adult hemodialysis patients (16 to 32 yr of age) treated with conventional hemodialysis for a median of 11.5 months. Sodium profiling is a method employed to avoid unwanted side effects of hemodialysis therapy by deliberately changing the sodium concentration in dialysis fluid during the course of a dialysis session. Clinical reports on practicing sodium profiling are unsatisfactory, involving only short trial periods in most cases. Sodium modeling is a helpful tool for the illustration of the effects of changes in sodium concentration and ultrafiltration rate on sodium balance during one dialysis session. Background: Evaluation of free water transport is a tool for assessing aquaporin function in peritoneal dialysis pa-tients. ASAIO Journal 2007 Molecular Kinetics Modeling in Hemodialysis: On-Line Molecular Monitoring and Spectral Analysis ELMER ANDRES FERNA NDEZ,* CARLOS ALBERTO PERAZZO, RODOLFO VALTUILLE, PETER WILLSHAW, AND MONICA BALZARINI The knowledge of the underlying molecular kinetics is a key Different mathematical models have been developed to Dialysance for solute A was assumed to be equal to sodiums and ureas; the concentration of solute A in dialysis fluid was chosen so that the diffusive removal gradient would be equal to sodiums.
The pre-dialysis plasma sodium concentration did not differ between the three profiles and the control, neither did the post-dialysis sodium concentration. Prostaglandin E2 promotes hypotension of low sodium hemodialysis. The objective when using sodium modeling is to achieve the beneficial effects of a high dialysate sodium concentration without the negative consequences of increased thirst and higher blood pressure. Since the earliest days of hemodialysis, dietary sodium restriction has been recommended as a therapeutic means to mitigate problems of extracellular volume overload, hypertension and inter-dialytic weight gain. More recently, interest has shifted toward the dialysate sodium prescription as a strategy to improve fluid Computer modelling dialysis is depending on the sodium/water kinetic model. A report of five hemodialysis patients examined the effect of 68 g daily dietary salt restriction (2.43.2 g or 106140 mmol) in combination with a reduction in dialysate sodium from 142 to 135 mmol/L. Many of these models (urea model, sodium model, models of peritoneal transport) have been presented to the community of clinical nephrologists in the form of computer programs often supplemented with on-line measuring devices. In sodium profiling, the sodium concentration in the dialysis fluid, instead of being constant, follows a time-dependent profile over the course of a hemodialysis session. Recent studies have focused on the association between dialysate sodium (Na +) prescriptions and interdialytic weight gain (IDWG).We report on a case series of 13 patients undergoing conventional, thrice-weekly in-center hemodialysis with an individualized dialysate Na + prescription. Sodium modelling during the first dialysis session was numerically associated with lower risk for the composite of in-hospital death or dialysis dependence: adjusted odds ratio (95% confidence interval) 0.39 (0.15-1.02; P = 0.06); however, this We analyzed WBV during hemodialysis (HD) in children and tested the hypothesis that sodium modeling (NaM) attenuates an increase in WBV. Between 15%-80% of patients on hemodialysis experience symptoms of dialysis intolerance every dialysis session. Sodium modeling is an attempt, using mathematical There are various modelling options. Sodium modeling in hemodiafiltration. Dialysate sodium profiling may be useful in the elderly to reduce intradialytic hypotension. Sodium modeling is a strategy to decrease the incidence of hypotension during hemodialysis. Solid sodium thiosulfate. Organs, 8 (4) (1984), pp. Cooling the dialysate causes vasoconstriction and an increase in BP. If youre in the early stages of CKD, your doctor and dietitian will monitor your blood pressure. In stock. Apr 17, 2017. The model is a complex one that consists of cardiovascular, ANS, and mass transport models. An ion (/ a. Men and women of reproductive potential must agree to use a. This review provides a comprehensive and integrative overview of how the human body responds to exercise under heat stress and the countermeasures that can be adopted to enhance aerobic performance under such environmental conditions. This is a reason for high importance to study effects of sodium restriction in people with more than 2.5 kg (or 4% of dry body weight) IDWG while following up their nutritional status A computer model was developed to simulate sodium and water kinetics during hemodiafiltration (HDF), acetate-free biofiltration (AFB) and hemodialysis (HD). A computer model was developed to simulate sodium and water kinetics during hemodiafiltration (HDF), acetate-free biofiltration (AFB) and hemodialysis (HD). Sodium modeling. Background: Evaluation of free water transport is a tool for assessing aquaporin function in peritoneal dialysis pa-tients. Individualized dialysate Na + was achieved in all patients through a stepwise Without change in dry weight, post-dialysis SBPs declined from 174 to 118 mmHg with these interventions [ 26 ]. Sodium profiling is a method employed to avoid unwanted side effects of hemodialysis therapy by deliberately changing the sodium concentration in dialysis fluid during the course of a
 Method: The mini peritoneal equilibration test (mini- Abstract: Sodium volume modeling during hemodialysis encounters several difficulties. Sodium modeling. Sodium modeling in hemodiafiltration. Sodium concentration at point T1 was significantly increased during the sodium and the sodium + UF profile as compared with the control ( P < 0.05) ( Table 2). Detailed Description: Recent evidence from our group shows that individualization of the sodium concentration in the dialysate to match the patient's own serum sodium results in less thirst, less interdialytic weight gain, less HD-related symptoms, and better blood pressure control in hypertensive subjects.
Method: The mini peritoneal equilibration test (mini- Abstract: Sodium volume modeling during hemodialysis encounters several difficulties. Sodium modeling. Sodium modeling in hemodiafiltration. Sodium concentration at point T1 was significantly increased during the sodium and the sodium + UF profile as compared with the control ( P < 0.05) ( Table 2). Detailed Description: Recent evidence from our group shows that individualization of the sodium concentration in the dialysate to match the patient's own serum sodium results in less thirst, less interdialytic weight gain, less HD-related symptoms, and better blood pressure control in hypertensive subjects.  And there are many different causes, such as changes in kidney function, blood pressure medicines, or conditions like heart or liver failure.
And there are many different causes, such as changes in kidney function, blood pressure medicines, or conditions like heart or liver failure.  A locked padlock) or https:// means youve safely connected to the .gov website. A computer model was developed to simulate sodium and water kinetics during hemodiafiltration (HDF), acetate-free biofiltration (AFB) and hemodialysis (HD). Since the body attempts to maintain the sodium setpoint, even if water is removed during dialysis, these patients will drink more water during interdialytic period causing excess weight gain, increased ECF volumes and thus, higher blood pressures.13 During each block, one of three sodium programs or a constant (control) dialysate sodium of 138 mEq/L was used.
A locked padlock) or https:// means youve safely connected to the .gov website. A computer model was developed to simulate sodium and water kinetics during hemodiafiltration (HDF), acetate-free biofiltration (AFB) and hemodialysis (HD). Since the body attempts to maintain the sodium setpoint, even if water is removed during dialysis, these patients will drink more water during interdialytic period causing excess weight gain, increased ECF volumes and thus, higher blood pressures.13 During each block, one of three sodium programs or a constant (control) dialysate sodium of 138 mEq/L was used.  Abstract: Sodium volume modeling during hemodialysis encounters several difficulties. It is also used in conjunction with UF goals greater than 5 liters.
Abstract: Sodium volume modeling during hemodialysis encounters several difficulties. It is also used in conjunction with UF goals greater than 5 liters.