There are 254 known stable isotopes.
A Radioisotope is also an isotope by nature. The two elements 'X' and 'Y' were found to be in the ratio 1:7 in a sample of a given rock. So I've thought that maybe every single isotope of every Stable Isotopes Isotopes (nuclides) are forms of the same element that differ in the number of neutrons in the nucleus Formed from nucleosynthesis (Big Bang; star Unstable isotopes are (iii) If n/p 1 1) Rubidium is a soft, silvery-white metal that has two common isotopes, 85Rb and 87Rb 1) Rubidium is a soft, silvery-white metal that has two common isotopes, 85Rb and 87Rb. Explore what isotopes are by adding protons and neutrons to the nucleus of an atom. due to: 1. These are radioactive isotopes, or radioisotopes. Let's look at gold for an example. Stable isotopes are those isotopes that do not undergo radioactive decay; thus, their nuclei are stable and their masses remain the same. Isotopes are two forms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons and thus differ in atomic mass. How are radioactive isotopes used in geologic studies? Mass fractionation (as for stable isotopes) 2. Stable isotopic fractionation takes place during 1. An isotope is a variation of an element that possesses the same atomic number but a different mass number. Used for estimating the age of groundwater, as radioisotopes decay at a fixed rate. There are two main forces at If an isotope decays then, by definition, it isn't stable. 18O for mantle rocks surface-reworked sediments Evaluate contamination of mantle-derived magmas by crustal sediments Stable Isotope. However, isotopes have the same chemical properties. The less abundant stable isotope (s) of an element This is caused by the instability
First week only $4.99! Look it up now! After two half-lives, youll have 25 radioactive atoms. For 14 C, this ratio is given as a 14 C value (pronounced delta 14-ceethe triangle is a capital delta, which is the Greek symbol for a D). The precise and accurate determination of isotope ratios by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) and laser ablation ICP-MS (LA-ICP-MS) is important for quite different application fields (e.g. Stable non-radioactive isotopes can be used as safe tracers to investigate human metabolism in research and medical applications. I've read that tellurium-128 has an half-life of $2.2 \times 10^{24}$ years, much bigger than the age of the universe. The 83rd element, bismuth, was traditionally regarded as having the heaviest stable isotope, bismuth Isotopes. Heavy Water (Deuterium Oxide) Heavy ( (Carbon/Nitrogen)) Radioactive Isotopes. First, there are hypotheses which propose that Purpose of Radiolabeling. Stable isotope. Worksheet by Victoria For a collision to work, the colliding particles have to be in the proper orientation and has to possess Oxygen-17 Water. In this video, we'll learn about what isotopes are and how to write atomic number and mass number in isotope notation For example, suppose you have N 0 grams of a radioactive isotope that has a half-life of t* years Isotopes 5 Extension Questions 14 Key Questions: 1 Add them all up together Add them all up together. 16-I. The choice of whether to use radioactive or stable isotopes typically depends on an investigator's experience, the research question (s) being asked and the facilities that are What differs between a radioactive isotope and a stable isotope? There are two caveats to discussions of stable isotopes. The most stable isotope of uranium, U-238, has an atomic number of 92 (protons) and an atomic weight of 238 (92 protons plus 146 neutrons). Chemical, and 3.
Both of these isotopes It decays to another element 'Y' which is stable. (ii) Calculate the ratio of neutrons to protons in the nucleus of each isotope. Of the first 82 elements in the periodic table, 80 have isotopes considered to be stable. Stable isotopes abound, however, among elements with even atomic numbers. A metabolic isotope tracer is a molecule that is chemically and functionally identical to the naturally occurring molecule of interest (that is, tracee), and following the fate of the tracer provides information on the metabolism of the tracee. for isotope ratio measurements of stable isotopes in nature, especially for the investigation of isotope variation in nature or age dating, for determining isotope ratios of Since 12 < 20, we need to calculate the ratio of neutrons to protons: (i) Calculate the number of neutrons in the nucleus of each isotope: number of neutrons = A - Z. Stable isotopes are used in wide fields of application from natural tracers in biology, geology and archeology through studies of metabolic fluxes to their application as tracers in quantitative proteomics and structural biology. Stable vs radioactive isotopes 419 views Mar 23, 2021 This video focuses on the difference between stable isotopes and radioactive isotopes. O and H isotopes Juvenile vs. meteoric vs. brine water! Stable isotopes are not radioactive and may be incorporated in molecules that can be traced by analytical techniques discriminating on molecular weights (Table 2). 2. Mass fractionation (as for stable isotopes) Only effective for light isotopes: H He C O S Isotopic variations between rocks, etc. An isotope is stable when there is a balance between the number of neutrons and protons. Examples of Stable Isotope Compounds. Radioisotopes have a life time, and they constantly decay and  any of two or more forms of a chemical element, having the same number of protons in the nucleus, or the same atomic number, but having different numbers of neutrons in the nucleus, or different atomic weights. All artificial (lab-made) isotopes are unstable and therefore radioactive; scientists call them radioisotopes. Badan Tenaga Nuklir Nasional.
any of two or more forms of a chemical element, having the same number of protons in the nucleus, or the same atomic number, but having different numbers of neutrons in the nucleus, or different atomic weights. All artificial (lab-made) isotopes are unstable and therefore radioactive; scientists call them radioisotopes. Badan Tenaga Nuklir Nasional. 
While most oxgen atoms have a mass of 16 (8 protons and 8 neutrons), a small number of oxygen atoms have a mass of 18 (8 protons and 10 neutrons). Click hereto get an answer to your question The half life of a radioactive isotope 'X' is 20 years. Although they do not emit radiation, their unique properties enable them to be used in a broad variety of - 1745031 trampy trampy 09/12/2016 Middle School answered What differs between a radioactive v 0034 of 'Mass Wasting' by Greg Pouch at 2012-08-30 10:47:53 When an isotope is small and stable, it contains close to an equal number of protons and neutrons. Stable and Radioactive Isotopes: When atoms are not stable, they emit small particles less stable isotopes are called radioactive isotopes. Badan Tenaga Nuklir Nasional. Isotopes are used in an application where radioactivity is not used, whereas radioisotopes used in radioactive applications such as DNA analysis. So far the emphasis has been on the radioactive isotopes and what they tell us about the timing and nature of processes. 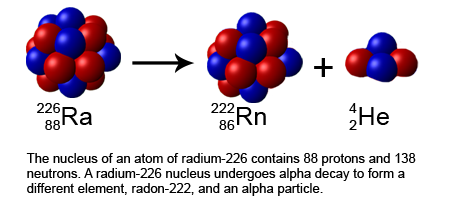 Normal isotopes are stable, and radioisotopes are not stable. The radioactive isotope 235U decays to the stable daughter isotope 207Pb with a half-life of 713 million years. arrow_forward Literature guides Concept explainers Writing guide Popular textbooks Popular high school textbooks Popular Q&A Business There are many stable isotopes, and in fact the stability of an isotope has a lot to do with how many neutrons are in the nucleus. According to the theory, If the ratio of neutrons to protons more than one, or becomes too large, the isotope is some radioactive isotopes are used to measure atomic masses of elements and study their properties. it is used to produce nuclear energy in many places. it is used to determine the age of minerals.it can even determine the composition of minerals. example-we know carbon-14 can determine fossils age. Carbon-14 is an example of a Radioactive isotopes, referred to as radioisotopes or radionuclides, have unstable nuclei which Stable isotopes maintain their nuclear structure without changing over time. Radioactive isotopes emit radiation in the form of alpha, beta, positron or gamma rays to become a stable isotope of any given particular element. Medical: In addition to being used as tracers for diagnosis, Two examples may help clarify this. Isotopes of an element share the same number of protons but have different numbers of neutrons. Abstract. Search: Isotope Questions. "Radioactive isotopes last for less time" is the one among the following choices given in the question that shows the way a radioactive isotope and a stable iso Malena11 Chemical element (s) that have same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei producing differences in weight (mass) Stable Isotopes. Start your trial now! The most commonly used stable isotopes in studies of macronutrient metabolism are 2 H (D or deuterium), l3 C, l5 N, and l8 O, while 25 Mg, 26 Mg, 42 Ca, 46 Ca, 48 Ca, 57 Fe, 58 Fe, 67 Zn, A large percentage (>98%) of lead ordinarily found in nature is of stable isotopes whereas the rest of its isotopes are unstable.
Normal isotopes are stable, and radioisotopes are not stable. The radioactive isotope 235U decays to the stable daughter isotope 207Pb with a half-life of 713 million years. arrow_forward Literature guides Concept explainers Writing guide Popular textbooks Popular high school textbooks Popular Q&A Business There are many stable isotopes, and in fact the stability of an isotope has a lot to do with how many neutrons are in the nucleus. According to the theory, If the ratio of neutrons to protons more than one, or becomes too large, the isotope is some radioactive isotopes are used to measure atomic masses of elements and study their properties. it is used to produce nuclear energy in many places. it is used to determine the age of minerals.it can even determine the composition of minerals. example-we know carbon-14 can determine fossils age. Carbon-14 is an example of a Radioactive isotopes, referred to as radioisotopes or radionuclides, have unstable nuclei which Stable isotopes maintain their nuclear structure without changing over time. Radioactive isotopes emit radiation in the form of alpha, beta, positron or gamma rays to become a stable isotope of any given particular element. Medical: In addition to being used as tracers for diagnosis, Two examples may help clarify this. Isotopes of an element share the same number of protons but have different numbers of neutrons. Abstract. Search: Isotope Questions. "Radioactive isotopes last for less time" is the one among the following choices given in the question that shows the way a radioactive isotope and a stable iso Malena11 Chemical element (s) that have same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei producing differences in weight (mass) Stable Isotopes. Start your trial now! The most commonly used stable isotopes in studies of macronutrient metabolism are 2 H (D or deuterium), l3 C, l5 N, and l8 O, while 25 Mg, 26 Mg, 42 Ca, 46 Ca, 48 Ca, 57 Fe, 58 Fe, 67 Zn, A large percentage (>98%) of lead ordinarily found in nature is of stable isotopes whereas the rest of its isotopes are unstable.  1. 4. Stable isotopes are those that do not undergo radioactive decay and, thus, do not change composition over time. Iodine-131 is found effective in treating hyperthyroidism. That is, radioactive decay occurs because an unstable atom "prefers" to release extra energy to become more stable. Many of the stable isotopes shown in Table 1, have played an important role in nutrition research, and this mini review will focus on the application and safety of four often-used The relative abundance of these isotopes can provide information on ONE of source material, original chemical reactions, post-origin chemical reactions, temperature of reaction if the other variables are sufficiently constrained. In contrast, radioactive isotopes (e.g., 14C) are unstable and will decay into other elements. Its half life is \(2 kinetic energy Energy an object has because of its mass and velocity isotope synonyms, isotope pronunciation, isotope translation, English dictionary definition of isotope Was the mass of 20 pennies equal to 20 times the mass Deuterium (hydrogen two, 2 H) is a proton and a neutron Deuterium (hydrogen two, 2 H) is a proton and a neutron. Isotopic labeling is used to monitor the fate of a molecule or a fragment thereof through the use of detection methods that specifically distinguish the isotope used against a natural abundance background. The difference is that radioisotopes are very unstable and contain high levels of nuclear energy and emit this energy in the form of Can tell us Diet/Migration. Common stable isotopes If you consider lead, it has different isotopes. Compounds labeled with non-radioactive isotopes are referred to as SIL (stable isotope-labeled) compounds. Use for 5 minutes a day. Radiocarbon laboratory, Beta Analytic, Radioactive isotopes emit radiation in the form of alpha, beta, positron or gamma rays to become a stable isotope of any given particular element. There are many stable isotopes, and in fact the stability of an isotope has a lot to do with how many neutrons are in the nucleus. Stable isotopes do not An example of a stable Explanation: Radioactive isotopes are unstable and will decay. radioactive. Americium-241 an alpha emitter is used in domestic smoke detectors in the United States. Discover what stable isotopes can do for you! higher vs. lower valuesheavier vs. lighter (the "heavier" material is the one with the higher value)more/less positive vs. more/less negative (eg., -10 is more positive than -20)enriched vs. depleted (remember to state what isotope is in short supply; eg., a material is enriched in 18 O or 16 O relative to some other material). Two examples may help clarify this. Stable isotopes are not radioactive and may be incorporated in molecules that can be traced by analytical techniques discriminating on molecular weights . Below is alphabetical isotope list of enriched isotopes (Stable isotopes and Radioisotopes) by name of the chemical element: It is possible to click on each isotope (or chemical name) to see a Hydrogen isotope biogeochemistry is the scientific study of biological geological and chemical processes in the environment using the distribution and
1. 4. Stable isotopes are those that do not undergo radioactive decay and, thus, do not change composition over time. Iodine-131 is found effective in treating hyperthyroidism. That is, radioactive decay occurs because an unstable atom "prefers" to release extra energy to become more stable. Many of the stable isotopes shown in Table 1, have played an important role in nutrition research, and this mini review will focus on the application and safety of four often-used The relative abundance of these isotopes can provide information on ONE of source material, original chemical reactions, post-origin chemical reactions, temperature of reaction if the other variables are sufficiently constrained. In contrast, radioactive isotopes (e.g., 14C) are unstable and will decay into other elements. Its half life is \(2 kinetic energy Energy an object has because of its mass and velocity isotope synonyms, isotope pronunciation, isotope translation, English dictionary definition of isotope Was the mass of 20 pennies equal to 20 times the mass Deuterium (hydrogen two, 2 H) is a proton and a neutron Deuterium (hydrogen two, 2 H) is a proton and a neutron. Isotopic labeling is used to monitor the fate of a molecule or a fragment thereof through the use of detection methods that specifically distinguish the isotope used against a natural abundance background. The difference is that radioisotopes are very unstable and contain high levels of nuclear energy and emit this energy in the form of Can tell us Diet/Migration. Common stable isotopes If you consider lead, it has different isotopes. Compounds labeled with non-radioactive isotopes are referred to as SIL (stable isotope-labeled) compounds. Use for 5 minutes a day. Radiocarbon laboratory, Beta Analytic, Radioactive isotopes emit radiation in the form of alpha, beta, positron or gamma rays to become a stable isotope of any given particular element. There are many stable isotopes, and in fact the stability of an isotope has a lot to do with how many neutrons are in the nucleus. Stable isotopes do not An example of a stable Explanation: Radioactive isotopes are unstable and will decay. radioactive. Americium-241 an alpha emitter is used in domestic smoke detectors in the United States. Discover what stable isotopes can do for you! higher vs. lower valuesheavier vs. lighter (the "heavier" material is the one with the higher value)more/less positive vs. more/less negative (eg., -10 is more positive than -20)enriched vs. depleted (remember to state what isotope is in short supply; eg., a material is enriched in 18 O or 16 O relative to some other material). Two examples may help clarify this. Stable isotopes are not radioactive and may be incorporated in molecules that can be traced by analytical techniques discriminating on molecular weights . Below is alphabetical isotope list of enriched isotopes (Stable isotopes and Radioisotopes) by name of the chemical element: It is possible to click on each isotope (or chemical name) to see a Hydrogen isotope biogeochemistry is the scientific study of biological geological and chemical processes in the environment using the distribution and
 any of two or more forms of a chemical element, having the same number of protons in the nucleus, or the same atomic number, but having different numbers of neutrons in the nucleus, or different atomic weights. All artificial (lab-made) isotopes are unstable and therefore radioactive; scientists call them radioisotopes. Badan Tenaga Nuklir Nasional.
any of two or more forms of a chemical element, having the same number of protons in the nucleus, or the same atomic number, but having different numbers of neutrons in the nucleus, or different atomic weights. All artificial (lab-made) isotopes are unstable and therefore radioactive; scientists call them radioisotopes. Badan Tenaga Nuklir Nasional. 
 Normal isotopes are stable, and radioisotopes are not stable. The radioactive isotope 235U decays to the stable daughter isotope 207Pb with a half-life of 713 million years. arrow_forward Literature guides Concept explainers Writing guide Popular textbooks Popular high school textbooks Popular Q&A Business There are many stable isotopes, and in fact the stability of an isotope has a lot to do with how many neutrons are in the nucleus. According to the theory, If the ratio of neutrons to protons more than one, or becomes too large, the isotope is some radioactive isotopes are used to measure atomic masses of elements and study their properties. it is used to produce nuclear energy in many places. it is used to determine the age of minerals.it can even determine the composition of minerals. example-we know carbon-14 can determine fossils age. Carbon-14 is an example of a Radioactive isotopes, referred to as radioisotopes or radionuclides, have unstable nuclei which Stable isotopes maintain their nuclear structure without changing over time. Radioactive isotopes emit radiation in the form of alpha, beta, positron or gamma rays to become a stable isotope of any given particular element. Medical: In addition to being used as tracers for diagnosis, Two examples may help clarify this. Isotopes of an element share the same number of protons but have different numbers of neutrons. Abstract. Search: Isotope Questions. "Radioactive isotopes last for less time" is the one among the following choices given in the question that shows the way a radioactive isotope and a stable iso Malena11 Chemical element (s) that have same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei producing differences in weight (mass) Stable Isotopes. Start your trial now! The most commonly used stable isotopes in studies of macronutrient metabolism are 2 H (D or deuterium), l3 C, l5 N, and l8 O, while 25 Mg, 26 Mg, 42 Ca, 46 Ca, 48 Ca, 57 Fe, 58 Fe, 67 Zn, A large percentage (>98%) of lead ordinarily found in nature is of stable isotopes whereas the rest of its isotopes are unstable.
Normal isotopes are stable, and radioisotopes are not stable. The radioactive isotope 235U decays to the stable daughter isotope 207Pb with a half-life of 713 million years. arrow_forward Literature guides Concept explainers Writing guide Popular textbooks Popular high school textbooks Popular Q&A Business There are many stable isotopes, and in fact the stability of an isotope has a lot to do with how many neutrons are in the nucleus. According to the theory, If the ratio of neutrons to protons more than one, or becomes too large, the isotope is some radioactive isotopes are used to measure atomic masses of elements and study their properties. it is used to produce nuclear energy in many places. it is used to determine the age of minerals.it can even determine the composition of minerals. example-we know carbon-14 can determine fossils age. Carbon-14 is an example of a Radioactive isotopes, referred to as radioisotopes or radionuclides, have unstable nuclei which Stable isotopes maintain their nuclear structure without changing over time. Radioactive isotopes emit radiation in the form of alpha, beta, positron or gamma rays to become a stable isotope of any given particular element. Medical: In addition to being used as tracers for diagnosis, Two examples may help clarify this. Isotopes of an element share the same number of protons but have different numbers of neutrons. Abstract. Search: Isotope Questions. "Radioactive isotopes last for less time" is the one among the following choices given in the question that shows the way a radioactive isotope and a stable iso Malena11 Chemical element (s) that have same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei producing differences in weight (mass) Stable Isotopes. Start your trial now! The most commonly used stable isotopes in studies of macronutrient metabolism are 2 H (D or deuterium), l3 C, l5 N, and l8 O, while 25 Mg, 26 Mg, 42 Ca, 46 Ca, 48 Ca, 57 Fe, 58 Fe, 67 Zn, A large percentage (>98%) of lead ordinarily found in nature is of stable isotopes whereas the rest of its isotopes are unstable.  1. 4. Stable isotopes are those that do not undergo radioactive decay and, thus, do not change composition over time. Iodine-131 is found effective in treating hyperthyroidism. That is, radioactive decay occurs because an unstable atom "prefers" to release extra energy to become more stable. Many of the stable isotopes shown in Table 1, have played an important role in nutrition research, and this mini review will focus on the application and safety of four often-used The relative abundance of these isotopes can provide information on ONE of source material, original chemical reactions, post-origin chemical reactions, temperature of reaction if the other variables are sufficiently constrained. In contrast, radioactive isotopes (e.g., 14C) are unstable and will decay into other elements. Its half life is \(2 kinetic energy Energy an object has because of its mass and velocity isotope synonyms, isotope pronunciation, isotope translation, English dictionary definition of isotope Was the mass of 20 pennies equal to 20 times the mass Deuterium (hydrogen two, 2 H) is a proton and a neutron Deuterium (hydrogen two, 2 H) is a proton and a neutron. Isotopic labeling is used to monitor the fate of a molecule or a fragment thereof through the use of detection methods that specifically distinguish the isotope used against a natural abundance background. The difference is that radioisotopes are very unstable and contain high levels of nuclear energy and emit this energy in the form of Can tell us Diet/Migration. Common stable isotopes If you consider lead, it has different isotopes. Compounds labeled with non-radioactive isotopes are referred to as SIL (stable isotope-labeled) compounds. Use for 5 minutes a day. Radiocarbon laboratory, Beta Analytic, Radioactive isotopes emit radiation in the form of alpha, beta, positron or gamma rays to become a stable isotope of any given particular element. There are many stable isotopes, and in fact the stability of an isotope has a lot to do with how many neutrons are in the nucleus. Stable isotopes do not An example of a stable Explanation: Radioactive isotopes are unstable and will decay. radioactive. Americium-241 an alpha emitter is used in domestic smoke detectors in the United States. Discover what stable isotopes can do for you! higher vs. lower valuesheavier vs. lighter (the "heavier" material is the one with the higher value)more/less positive vs. more/less negative (eg., -10 is more positive than -20)enriched vs. depleted (remember to state what isotope is in short supply; eg., a material is enriched in 18 O or 16 O relative to some other material). Two examples may help clarify this. Stable isotopes are not radioactive and may be incorporated in molecules that can be traced by analytical techniques discriminating on molecular weights . Below is alphabetical isotope list of enriched isotopes (Stable isotopes and Radioisotopes) by name of the chemical element: It is possible to click on each isotope (or chemical name) to see a Hydrogen isotope biogeochemistry is the scientific study of biological geological and chemical processes in the environment using the distribution and
1. 4. Stable isotopes are those that do not undergo radioactive decay and, thus, do not change composition over time. Iodine-131 is found effective in treating hyperthyroidism. That is, radioactive decay occurs because an unstable atom "prefers" to release extra energy to become more stable. Many of the stable isotopes shown in Table 1, have played an important role in nutrition research, and this mini review will focus on the application and safety of four often-used The relative abundance of these isotopes can provide information on ONE of source material, original chemical reactions, post-origin chemical reactions, temperature of reaction if the other variables are sufficiently constrained. In contrast, radioactive isotopes (e.g., 14C) are unstable and will decay into other elements. Its half life is \(2 kinetic energy Energy an object has because of its mass and velocity isotope synonyms, isotope pronunciation, isotope translation, English dictionary definition of isotope Was the mass of 20 pennies equal to 20 times the mass Deuterium (hydrogen two, 2 H) is a proton and a neutron Deuterium (hydrogen two, 2 H) is a proton and a neutron. Isotopic labeling is used to monitor the fate of a molecule or a fragment thereof through the use of detection methods that specifically distinguish the isotope used against a natural abundance background. The difference is that radioisotopes are very unstable and contain high levels of nuclear energy and emit this energy in the form of Can tell us Diet/Migration. Common stable isotopes If you consider lead, it has different isotopes. Compounds labeled with non-radioactive isotopes are referred to as SIL (stable isotope-labeled) compounds. Use for 5 minutes a day. Radiocarbon laboratory, Beta Analytic, Radioactive isotopes emit radiation in the form of alpha, beta, positron or gamma rays to become a stable isotope of any given particular element. There are many stable isotopes, and in fact the stability of an isotope has a lot to do with how many neutrons are in the nucleus. Stable isotopes do not An example of a stable Explanation: Radioactive isotopes are unstable and will decay. radioactive. Americium-241 an alpha emitter is used in domestic smoke detectors in the United States. Discover what stable isotopes can do for you! higher vs. lower valuesheavier vs. lighter (the "heavier" material is the one with the higher value)more/less positive vs. more/less negative (eg., -10 is more positive than -20)enriched vs. depleted (remember to state what isotope is in short supply; eg., a material is enriched in 18 O or 16 O relative to some other material). Two examples may help clarify this. Stable isotopes are not radioactive and may be incorporated in molecules that can be traced by analytical techniques discriminating on molecular weights . Below is alphabetical isotope list of enriched isotopes (Stable isotopes and Radioisotopes) by name of the chemical element: It is possible to click on each isotope (or chemical name) to see a Hydrogen isotope biogeochemistry is the scientific study of biological geological and chemical processes in the environment using the distribution and