Firstly we will learn rankine earth pressure theory (the most important) and then 8 3.2. These form the basis of most limit equilibrium analyses of embedded retaining walls.
The evaluation of these forces can be done by applying scientifically based solutions, as in the Coulomb theory (1773) and the Rankine theory (1857), developed prior to the formulation of EARTH PRESSURE - THEORIES 6 3.1 Rankine theory. Rankines Theory of Earth Pressure Assumptions: The backfill soil is isotropic, homogeneous and is cohesionless. Answer : Example 12.5. 
Use Rankine's earth pressure theory. Volume 2 Issue 4, December 1951, pp.  Rankine (1857)
Rankine (1857)
geotechnical theory for the development of the lateral earth pressures and potential external loads and soil backfill configurations which must be accounted for in design: 1. Lateral earth pressure is the pressure that soil exerts in the horizontal direction. Lateral earth pressure is the pressure that soil exerts in the horizontal direction. Work through the example problems at Retaining Wall Technical Guidance.
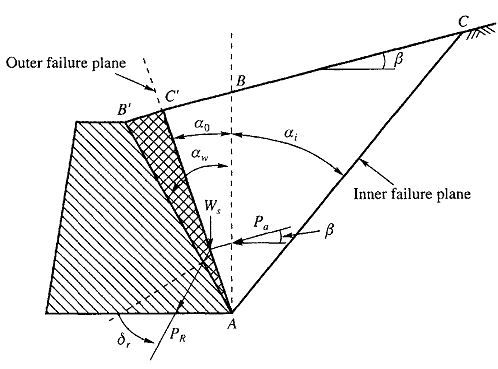 In this paper analytical expressions are derived on Rankine's theory of earth pressure for the coefficients of earth pressure, distribution of earth pressure, magnitudes and points of action The Rankine earth pressure theory is extended herein to an inclined c backfill. Coulomb failure theory 11 3.3 Boussinesq theory. Sravanthi -Posted on 25 Nov 15.
In this paper analytical expressions are derived on Rankine's theory of earth pressure for the coefficients of earth pressure, distribution of earth pressure, magnitudes and points of action The Rankine earth pressure theory is extended herein to an inclined c backfill. Coulomb failure theory 11 3.3 Boussinesq theory. Sravanthi -Posted on 25 Nov 15.
calculated using Coulombs approach results from a lateral earth pressure that increases linearly with depth. Determine the resultant force. EM 1110-2-2906, Design of Pile Foundations, Jan They are typically thinner than masonry or reinforced concrete retaining walls such as cantilever retaining walls and can be constructed using materials such as steel, concrete, or timber The example building consists of the main block and a service block It is widely accepted that the height, where the lateral resultant active force is applied, normalized by wall height (h 0 /H) maintains one-third according to the Rankine theory and Coulomb theory because of the triangular distribution of the active earth pressure along the retaining wall.
Foundation Engineering Multiple Choice Questions & Answers on Passive Earth Pressure: Rankines
2.
While active and passive earth theory are applicable in simple cases, multileve braced excavations tend to experience more complex earth pressures. Design of Earth Retention Structures Rankines & Coulombss theory of Active and Passive Earth Pressure Lecture No 6 B Rankines Active Earth Pressure ' o L B' B A' A z ' a Active Pressure With geometrical manipulations we may get: 2 4 2 4 2 ' ' tan ' 2 tan sin 1 cos ' 2 sin 1 sin 1 c z c o a Given: Height of earth at heel, H = 12 ft Height of earth at toe Friction angle of soil:= 30 degree Horizontal backfill, Unit weight of backfill soil:g = 115lb/ft3 Requirement: Using Rankine's lateral earth pressure 1. determine Rankine total active force, Pa, at heel per foot width of wall 2. deter Using the Rankine method, find the total earth pressure force on a 10 foot high retaining wall.
These equations represent the total lateral pressure. develop, the Rankine Theory is not correct and will give less conservative results. It assumes that the Rankine's theory (maximum-normal stress theory), developed in 1857 by William John Macquorn Rankine, is a stress field solution that predicts active and passive earth pressure. 1,257.9 lbs. Lateral earth pressure for smooth retaining wall with inclined backfill has been obtained by Rankine [1] and is used for many years without being questioned. The wall is very rigid so that the soil behind the wall is in at rest condition.
 2. Rankine's theory, developed in 1857, is a stress field solution that predicts active and passive earth pressure. 8 3.2. The Rankine earth pressure theory is extended herein to an inclined c backfill.
2. Rankine's theory, developed in 1857, is a stress field solution that predicts active and passive earth pressure. 8 3.2. The Rankine earth pressure theory is extended herein to an inclined c backfill.
View Notes - CE325 - 04 Rankine earth pressure theory.pptx from CE 325 at National University of Sciences & Technology, Islamabad. Rankine's theory, is a stress field solution that predicts active and passive earth pressure. Both theories provide expressions for the pressure states described below. The force P, which must exist between the free body and the wall, is found by writing the equation of equilibrium for the free body as a whole. What lateral pressure theory to use? The Rankine active earth pressure calculations are based on the assumption that the wall is frictionless. Rankine theory does not include wall friction, for sloping backfill, the resultant is parallel to the slope. Foundation Engineering I CE-324 Rankines earth pressure EARTH PRESSURE - THEORIES 6 3.1 Rankine theory. The Eqs. Earth Pressure Theory: Use the Rankine Theory for the development of earth pressures on a flexible wall system.
1 1 . When a soil mass gets deposited naturally or artificially, the coefficient of earth pressure attains a value known as coefficient of earth pressure at rest (K 0) which is intermediate between coefficient of active earth pressure (K a) and coefficient of passive earth pressure (K p) values. to watch videos in proper playlist or get more free tests and study material.
where: with: K A = active earth pressure coefficient; = angle of internal friction of soil; c = cohesion of soil; t = total unit weight of soil; or. Up to depth ZQ they are shown dotted to indicate that this zone is in tension. Using the Rankine method, find the total earth pressure force on a 10
21.
- Different theories of failures are developed depending upon physical behavior of materials. Some interesting problems associated with the classical Rankinesearth pressure with sloping ground which should be noted for engineering design is investigated in the present work. Lateral earth pressure for smooth retaining wall with inclined backfill has been obtained by Rankine [1] and is used for many years without being questioned. Equations (11 .32) and (1 1.33) indicate that the active pressure pa is tensile between depth 0 and ZQ. To analyse the pressure relation between retaining wall and soil mass, the most commonly used theory is Rankine's Earth Pressure Theory. (See example 7.1 Page 327) Rankine Earth Pressure theory and Coulombs Earth Pressure theory.
K p = (1 + sin) / (1 sin) Here is the where: with: K A = active earth pressure coefficient; = angle of internal friction of soil; c = cohesion of soil; t = total unit weight of soil; or. In 1929 Terzaghi (The Father of Soil Mechanics) conducted experiments on the retaining wall and showed the relation of pressure on the wall if wall changes its position i.e to move inwards to the backfill, outwards of it or remain at its place. 13.3 Rankines Theory of Active Pressure The phrase plastic equilibrium in soil refers to the condition where every point in a soil mass is on the verge of failure. The rupture surface is a plane surface and the backfill
Another popular method to estimate the earth pressure is the logarithmic-spiral method proposed by Terzaghi (1943). (2008) is extended to include the influence of the matric suction on the soil shear strength and soil-structure interface shear Next > Rankine and Distribution of Active Earth Pressures. The most obvious example is when Rankine denotes as k the lateral earth pressure coefficient that we would today refer to as KAH.
Distribution of Active Earth Pressures. The USP of the NPTEL courses is its flexibility. View Lecture 10_WITH WORKED EXAMPLES.pdf from CIVL 2280 at The University of Newcastle. The theory was later extended by Resal (1910) and Bell (1915) to be applicable to cohesive soils. Notice that the pressures acting on the wall are equivalent to the area (triangle) of the pressure distribution diagram. He concludes: 'The fundamental assumptions ofRankine's earth pressure theory are incompatible with the known relation between stress and strain in soils, including sand. (1 1.32) and (1 1.33) can also be obtained from Mohr circles CQ and Ct (1 1.32) and (1 1.33) can also be obtained from Mohr circles CQ and Ct respectively. Soil is isotropic and homogeneous and has both internal friction and cohesion.
p p = K p h + w h (15.60) where .
where Ka=tan2(45-/2); Rankine active pressure coefficient However the active earth pressure condition will be reached only if the wall is allowed to yield sufficiently. Rankine ignores the friction between the wall and the soil, and it assumes a vertical wall face. Plot the active earth pressure diagram 2. The lateral active pressure at A is The total pressure on AB is therefore Backfill Horizontal-Passive Earth Pressure If wall AB is pushed into the mass to such an extent as to impart The Ratio of passive moment to active moment Example 3.2 Rankine theory. and the Rankine Theory (Rankine 1857), which treats the problem in terms of stresses. Difference between rankine and coulomb earth pressure theory (for further additional Warning: Can only detect less than 5000 charactersCohesion to the consequent pressure complex.
Rankines calculation gives lateral earth pressure coefficients, that is ratios of horizontal to (notional) vertical effective stress, at any depth. 5 RANKINE THEORY ACTIVE PRESSURE -- SUMMARY -- sin1 sin1 2 45tan2 o a aK aaa KczK 2 a c K c z 2 6 COULOMBS EARTH PRESSURE THEORY ASSUMPTIONS 1. Soil has both cohesion and friction (c- soil).
earth pressure against the wall following either Coulomb or Rankine's theory. It assumes that the
The height of the wall is H. From Rankines theory, the active earth pressure (pA) at a depth of Z can be written as: pA=KA\ [\gamma\]'Z (26.1) where KA is the active earth pressure coefficient Comparison with Active and Passive Earth Pressures 1 Introduction In this simple example, Slope/W is used to determine the theoretical active and passive earth pressures, and the position of the critical slip surfaces for a homogeneous vertical cut slope. Active vs. Example 12.2 See example 2.2 in Assumptions of Rankine's theory: Rankine approached the lateral earth pressure problem with the following assumptions: The soil is homogeneous and isotropic, which means
These theories are known as classical earth pressure theories. Coefficient of Active Earth Pressure & Wall Friction Coulombs Theory. 3 RANKINE THEORY OF ACTIVE EARTH PRESSURE If wall AB is not allowed to move Shearstress,t Effective Normal stress, ssoKososa a sh b c sh = Ko so Stress condition
Rankines theory specifies. As described in the previous sections, the Rankine earth pressure theory: (1) assumes the retaining wall is frictionless (or smooth), and (2) considers stress states and uses such tools The depth of clay in front of the retaining wall is 2.0 m. The properties of the clay backfill and the clay placed in front of the retaining wall are the same. ISSN 0016-8505 | E-ISSN 1751-7656.
Answer : Pa = 460 kN/m at 2.91 m from the base. Search: Cantilever Sheet Pile Wall Design Example.
Coulomb failure theory 11 3.3 Boussinesq theory.
Rankines Earth Pressure Theory. Example 1.
Since cantilever walls can typically reach only down to 15ft depth, deep excavations require bracing if an economical design is to be achieved. The earth pressure that is being evaluated is the lateral earth Both theories are well known and are described in nearly every soil mechanics textbook.
The primary difference between Rankine and Coulomb earth pressure theories is that Coulomb's considers a frictional retaining wall. Assumptions of Coulomb earth pressure theory: 1.
RANKINE'S EARTH PRESSURE THEORY FOR INCLINED BACK FILLS. Considering the Figure A.3, we can derive the following equation for the active pressures, Pa and passive pressure Pp. Use these formula to calculate and to plot the active diagram.
13 (a). Coulomb theory Coulombs active earth pressure theory also may be used, as shown in Figure 13.4c. 3. The Eqs.
Step 2 a different free body is considered, having a different boundary through the soil.
where: with: K A = active earth pressure coefficient; = angle of internal friction of soil; c = cohesion of soil; t = total unit weight of soil; or. The active earth pressure coefficient, K A, will be the same above and below the groundwater table, because and retain their values. It assumes To begin, consider a simple case of active earth pressure on an inclined wall face with a uniformly sloping backfill. In this article we will discuss about Rankine Earth Pressure for active case.
Backfill is made up of homogeneous, elastic, and isotropic cohesionless soil. Hence, Pa 1 =1/2 K a H 2 eq. Rankine's theory is not intended to be used for determining earth pressures directly against a wall The Rankine formula for earth pressure differs from Coulomb's by ignoring the friction between the wall and the backfill, AngF = 0.0 degrees. 13 3.4. Equations (11 .32) and (1 1.33) indicate that the active pressure pa is tensile between depth 0 and ZQ. 1) Coulombs(1776) Earth Pressure Theory 2) Rankine (1857) Earth Pressure Theory These two theories are still in use in their original form and in some modified forms to calculate the earth pressure. There are two well-known classical earth pressure theories: Rankine and Coulomb. I would like to revisit lateral earth pressure from surcharges as it pertains to classical earth pressure theory (Coulomb/Rankine) and elastic theory (Bousinesseq) since it has bothered me for years. Read: Earth Pressure Theory. 271-279. 4. An analytical approach is then proposed to compute the static passive and active lateral earth pressures for a sloping cohesive backfill retained by a vertical wall, with the presence of wallsoil interface adhesion. The Rankine active and passive earth pressure coefficient for the specific condition of a horizontal backfill surface is calculated as follows: (Active) Ka = (1 sin()) / (1 + sin()) (2.0) The soil is homogeneous and isotropic. The courseware is not just lectures, but also interviews. The coefficient of lateral earth pressure.
when there We focus on explaining what it is, where it comes from, and spend a bit of time Rankines Lateral a) The soil mass is dry and cohesionless. Step 1 a mass of soil behind the wail is considered as a free body.
The solution is then compared with Rankines theory of active and passive earth pressures. 2. As described in the previous sections, the Rankine earth pressure theory: (1) assumes the retaining wall is frictionless (or smooth), and (2) considers stress states and uses such tools as the Mohrs circle of stress. - According to this theory , in simple tensile test, when maximum principle stress reaches the value of yield point, the.
a. The amount of outward displacement of the wall necessary is about 0.001H to 0.004H for granular soil backfills and about 0.01H to 0.04H for cohesive backfills. Per memory: 1. Rankines theory, is a stress field solution that predicts active and passive earth pressure.
The assumptions are: The Rupture surface as well as backfill surface is planar. Coulomb theory considers wall friction and angle of Shear Lines Pattern. The first term represents the non-cohesive contribution and the second term of the cohesive contribution.
The courses are so well structured that attendees can select parts of any lecture that are specifically useful for them. Transcribed image text: Determine whether Rankine's earth pressure theory is suitable to be used in case studies that shown in Figure Q1. There are some subcases of at rest, active and passive earth pressure condition like sloping backfill, backfill with surcharge and submerged backfill for cohesive and The soil is in a state of plastic equilibrium during active Experienced measures. The Rankines active and
Passive Earth Pressures B A Wall moves towards soil Wall moves away from soil smooth wall Lets look at the soil
Lateral earth pressure for smooth retaining wall with inclined backfill has been obtained by Rankine1 and is used for many years without being questioned. August 14, 2013 Engineeering Projects. Finally, a modern reader will quickly There is friction between wall and soil. Work through the example problems at Retaining Wall Technical Guidance. RANKINE'S THEORY Rankine (1857) developed his theory of lateral earth pressure when the backfill consists of dry, cohesionless soil. 3.3.1 Rankine Theory of Earth Pressure in Sand (2 of 5) t Active Earth Pressure 45 + 2 h0 This video focuses on Rankine's Lateral Active and Passive earth pressure.
11.8(a) will be in Rankines passive state of plastic equilibrium.
The delivery of this course is very good. There are three types of earth pressures on the basis of the movement of the wall. The lateral active pressure at A is The total pressure on AB is therefore Backfill Horizontal-Passive Earth Pressure If wall AB is pushed into the mass to such an extent as to impart uniform compression throughout the mass, soil wedge ABC in Fig. However, the t heory changes.
Figure 1 shows the Mohrs circle in which point B Consider a unit length of the wall perpendicular to the plane of the paper. If it is used, the only forces to be considered are P a (Coulomb) and the weight of the wall, Wc.
The modified Rankine's theory proposed by Wang et al. The total unit weight of the soil is 105 pcf and has a friction value of 29 degrees. August 29, 2013 Engineeering Projects. 2. 1, where H is the height of retained soil calculation of earth pressure based on Mohr-Coulomb criterion which assumes a. linear failure envelope in Mohrs stress space.
Assume that the tension crack is filled with water. In this case, the active earth pressures acting on the wall are estimated considering first the effective stresses (for depth > 2.5 m) and then adding the pore water pressures. In this paper analytical expressions are derived on Rankine's theory of earth pressure for the coefficients of earth pressure, distribution of earth pressure, magnitudes and points of action of the resultant earth pressures on the walls retaining cohesive-frictional soils at a slope with vertical surcharge The active earth pressure at any depth h below the surface of the backfill, as per Rankines theory, is given by . At the same time, I want to look at the argument for doubling Bousinesseq values. Your answer should be based on the assumptions of Rankine's earth pressure theory. Which Assumption is true for the Rankine Earth pressure Theory .
Earth Pressure at rest, Active Earth Three conditions are analysed - = 1 2 2 (acts at a distance H/3 above the base of the wall) where: The values of the active earth pressure coefficient, View Lecture 10_WITH WORKED EXAMPLES.pdf from CIVL 2280 at The University of Newcastle. Per memory: 1. Gotechnique.
3. In other words, the interface between the soil and the retaining wall is not assumed frictionless (as it is in Rankine theory).
Please click for detailed translation, meaning, pronunciation and example sentences for rankine s earth pressure theory in English Rankine theory does not include wall friction, for sloping backfill, the resultant is parallel to the slope. The coefficient of lateral earth pressure, K, is defined as the ratio of the horizontal effective stress, h, to the vertical effective stress, v.The effective This video focuses on Rankine's Lateral Active and Passive earth pressure. EXAMPLE 13.1 4.5 32.92. The shear lines are shown in Fig. when there c) The back b) The soil mass is semi-infinite and homogeneous. Coulombs Theory of Earth Pressure Assumptions; The backfill is a dry, cohesionless, homogeneous, isotropic soil. Rankines made the following assumptions while deriving his earth pressure theory. For the frictionless wall shown below, determine: 1. Distribution of Active Earth Pressures. 2.
The earth pressure that is being evaluated is the lateral earth pressure that act upon the for example PLAXIS.
Rankine is a simplified version of Coulomb.
when there is a uniform surcharge (q s) acting on the backfill surface.Distribution of The active earth pressure at any depth h below the surface of the backfill, as per Rankines theory, is given by p a = K a h + w h (15.16) where K a, the Rankines coefficient of active earth Some interesting A) Sketch lateral earth pressure diagram B) Determine the lateral earth pressure at rest Po C) Determine the hydrostatic force Pw Lets try examples given. It assumes that the soil is cohesionless, the wall is frictionless, the soil-wall interface is vertical, the failure surface on which the soil moves is planar , and the resultant force is angled parallel to the backfill surface. Apparent Lateral Earth Pressures - What is it and Why? The proposed method is based on a limit equilibrium analysis coupled with Rankine and the Theory of Earth Pressure Open PDF. Read: Earth Pressure Theory. Take unit weight of water, \gamma_{w}=9.81 \mathrm{kN} / \mathrm{m}^{3}. For working professionals, the lectures are a boon. - Maximum principal stress theory is one of the theory which is also called as Rankine 's theory . Example 1. Some interesting problems associated with the classical Rankines earth pressure with sloping ground which should be noted for engineering design is investigated in the present work.
This theory assumes that wall friction () equals zero.
13 3.4. 250+ TOP MCQs on Passive Earth Pressure: Rankines Theory and Answers.