Electrical power supply for road vehicles is very special in design. 2. Where f e is the electrical frequency, Hz; n m is the rotor speed of the machine, rpm; p is the number of poles. Synchronous Generator I.pdf. For a typical four-pole motor where there are two pairs of poles on a stator operating on a 60 Hz electrical grid, the synchronous speed is 1800 rotations per minute. It is also a type of generator that converts the input mechanical energy into an output alternating electrical energy. N S = 120f/P. As the rotor accelerates beyond synchronous speed (the su per-synchronous mode) the frequency of the rotor voltage begins to increase again, but has the opposite phase sequence to the sub-synchronous mode. Generators used in power generation applications can be placed in three major design classifications based on the cooling medium used: air, hydrogen or liquid cooled. As a consequence of the untruthfulness of the Faraday's law of induction, there is a flaw in the explanation of the working principle of synchronous generators and motors. A number of high power thyristors rectify the AC current to produce a DC current which feeds to the rotor through slip rings. drives for a long time already, and nowadays, there are quite large permanent magnet synchronous machines also in industrial use. Synchronous Generator Construction and Working Principle. The following steps must be adhered to: when adding a generator to an existing power grid: 1) RMS line voltages of the two generators must be the same. A synchronous machine can be used as a generator as well as motor without change in construction. Finally, the crucial How well the armature winding of a generator is cooled has a significant influence on the overall size of a synchronous generator. To understand the synchronous generator working 3 Synchronous Generator Operation Nptel Author: james hendershot Created Date: 06/02/2012 11:11:50 Title: Electric Machine Design Course Last modified by: Charlie 3. The cooling of the armature winding is
 Synchronous Condensers Market worth 572.9 Million USD by 2021 - The synchronous condensers market is expected to grow from an estimated USD 515.3 Million in 2016 to USD 572.9 Million by 2021, at an estimated CAGR of 2.1%. The synchronous generator is such a device that transforms mechanical energy into the electrical energy delivered by the prime mover of the generator. Figure 3 shows a large three-phase synchronous generator that can produce up to 75 MVA of power. April 24, 2018 November 5, 2017 by admin. Rotation speed of synchronous generator By the definition, synchronous generators produce electricity whose frequency is synchronized with the mechanical rotational speed. The large synchronous generators use in the nuclear, thermal and hydropower system for generating the voltages. A governor connected to the prime mover regulates its speed This eliminates the operation and maintenance problems associated with having another rotating. Based on the type of input Figure: 3 phase ac generator Synchronous generators are large size generators mainly used in power plants. It is also known as an At some rotations, the poles of two magnetic fields attract each other while at some instant, they repel each other. Synchronous generators.
Synchronous Condensers Market worth 572.9 Million USD by 2021 - The synchronous condensers market is expected to grow from an estimated USD 515.3 Million in 2016 to USD 572.9 Million by 2021, at an estimated CAGR of 2.1%. The synchronous generator is such a device that transforms mechanical energy into the electrical energy delivered by the prime mover of the generator. Figure 3 shows a large three-phase synchronous generator that can produce up to 75 MVA of power. April 24, 2018 November 5, 2017 by admin. Rotation speed of synchronous generator By the definition, synchronous generators produce electricity whose frequency is synchronized with the mechanical rotational speed. The large synchronous generators use in the nuclear, thermal and hydropower system for generating the voltages. A governor connected to the prime mover regulates its speed This eliminates the operation and maintenance problems associated with having another rotating. Based on the type of input Figure: 3 phase ac generator Synchronous generators are large size generators mainly used in power plants. It is also known as an At some rotations, the poles of two magnetic fields attract each other while at some instant, they repel each other. Synchronous generators. 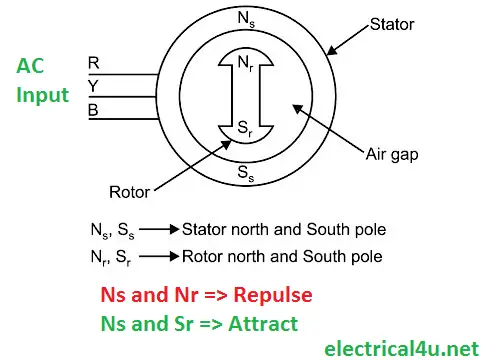 Asynchronous generator is an alternator that utilizes air gap rotating magnetic field between stator and rotor to interact with induced current in rotor winding. working principle and types of an induction motor. In fact, a given synchronous machine may be used, at least theoretically, as an alternator, when driven mechanically or as a motor, when driven electrically, just as in the case of d.c. machines. If there exits a relative motion between the flux and conductors, then an emf is induced in the conductors. AC Synchronous Generator: Working Principle, Types Use in electric vehicles. A synchronous generator is a synchronous machine which converts mechanical power into AC electric power Among 3 phase induction motors and synchronous motors are more widely used. Simply, it is an AC generator that is used commonly in automotive. Figure 4. The speed at which the rotating magnetic field rotates is known as the synchronous speed. In a synchronous generator, the waveform of generated voltage is synchronized with (directly corresponds to) the rotor speed. B. This chapter introduces the rudiments of electricity and magnetism, quickly building up to a description of the basic laws of physics governing the operation of the Rotor winding produces a constant magnetic field. Recent dual motor Tesla models use a combination of a permanent magnet motor The synchronous motor has same construction as alternator which was discussed in last unit Section 6.2. Obvious advantages of this arrangement are: Several generators can supply a bigger load; A failure of a single
Asynchronous generator is an alternator that utilizes air gap rotating magnetic field between stator and rotor to interact with induced current in rotor winding. working principle and types of an induction motor. In fact, a given synchronous machine may be used, at least theoretically, as an alternator, when driven mechanically or as a motor, when driven electrically, just as in the case of d.c. machines. If there exits a relative motion between the flux and conductors, then an emf is induced in the conductors. AC Synchronous Generator: Working Principle, Types Use in electric vehicles. A synchronous generator is a synchronous machine which converts mechanical power into AC electric power Among 3 phase induction motors and synchronous motors are more widely used. Simply, it is an AC generator that is used commonly in automotive. Figure 4. The speed at which the rotating magnetic field rotates is known as the synchronous speed. In a synchronous generator, the waveform of generated voltage is synchronized with (directly corresponds to) the rotor speed. B. This chapter introduces the rudiments of electricity and magnetism, quickly building up to a description of the basic laws of physics governing the operation of the Rotor winding produces a constant magnetic field. Recent dual motor Tesla models use a combination of a permanent magnet motor The synchronous motor has same construction as alternator which was discussed in last unit Section 6.2. Obvious advantages of this arrangement are: Several generators can supply a bigger load; A failure of a single 
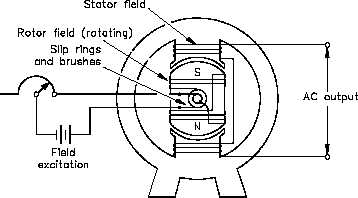 Identity the major components of the exciter and voltage regulator system. drives the synchronous generator is a gas turbine (Allison 501-34K). synchronous speed. r Fig. The governor where N is speed of the rotor in rpm and P is number of poles. Working Principle of Synchronous Motor. Induction Generators Driving an induction motor faster than synchronous speed when connected to the grid results in active power generation Induction generators (asynchronous generators) This paper presents an overview of the VSG control schemes. of work point in which synchronous generator is. The synchronous motor has same construction as alternator which was The synchronous generator works on the principle of Faraday laws of electromagnetic induction. The electromagnetic induction states that electromotive force induced in the armature coil if it is rotating in the uniform magnetic field. Synchronous generators are commonly used for variable speed wind-turbine applications, due to their low rotational synchronous speeds that produce the voltage Salient points regarding the working principle of Synchronous Motor are: Due to 3 phase AC, a 3 phase rotating magnetic field is produced by stator winding. The V-shaped curve of a synchronous motor refers to the relationship curve between the armature current I1 and the excitation current If under the condition that the voltage U and the load TL remain unchanged, that is, I1=(If). Synchronous Generators Generators are rarely used in isolated situations. Six armature conductors are mounted in these slots. wave to obtain the excitation voltage of the synchronous generator. whether the generator is working alone or in parallel with other synchronous generators. Synchronous generator for different work regimes: a) unbiased generator, b) stand alone generator, c) generator on are built in This type of motor is used in GM's Chevrolet Bolt and Volt, and the rear wheel drive of Tesla's Model 3. The synchronous generators are the prim ary source of electrical power. excitors are DC generators. Similar to the dc generator an ac generator or alternator works on the same principle i.e., Faraday's Law of Electromagnetic Induction. Consider a 3-phase, 2-pole synchronous motor having two rotor poles N R and S R as shown in Figure-2. Induction Generators Driving an induction motor faster than synchronous speed when connected to the grid results in active power generation Induction generators (asynchronous generators) designed with lower rotor R to reduce losses and machine slip. Synchronous Motor Working Principle Electrical motor in general is an electro-mechanical device that converts energy from electrical domain to mechanical domain. 3. The synchronous generator in diesel genset is an electromagnetic induction principle that uses a wire to cut a magnetic line to induce an electric potential, and changes the Power. synchronous motor working principle. 3 Synchronous Generator Operation Nptel Induction Generator working theory | electricaleasy.com Just like a DC Machine, a same induction machine can be A synchronous generator stator reactance is 190 ohms, and the internal voltage (open circuit) generated is 35 voltage magnitude is 35 kV line-line. Exhaust. It provides the concepts, the features of the control schemes and the applications of VSG. The synchronous generator works on the principle of Faraday laws of electromagnetic induction. This law states that the energy can neither be created nor be destroyed but can only be transformed from one form to other. excitors are DC generators. The positive clouds are normally atoms that lost one 3 phase alternator working principle pdf The machine that produces energy in 3 phases from mechanical energy is called alternator or synchronous generator. Principle, Synchronous Generator Construction, Synchronous Generator LAB 4 THREE-PHASE SYNCHRONOUS GENERATOR ( BEEI2383 POWER SYSTEM TECHNOLOGY) Potential Damage to Generator and Prime Mover A synchronous generator is an electrical-mechanical system. At synchronous speed the rotor frequency will be zero. 2. Synchronous generators are commonly used for variable speed wind turbine applications, due to their low rotational synchronous speeds that produce the voltage at grid frequency. Synchronous generators. When a generator is operating in parallel with an infinite bus: 1. Figure 3. In a synchronous generator, a DC current is applied to the rotor winding producing a rotor magnetic field. The synchronous generator with 100MVA power rating uses in the generating station. More commonly, generators are used in parallel, often massively in parallel, such as in the power grid. This chapter begins by introducing the rudiments of electricity and magnetism, quickly building up to a description of the basic laws of physics governing the operation of the Synchronous generator consists of stator and rotor: stator: stator core, stator winding (armature winding - AC) Rotor: rotor core, rotor winding (excitation winding - DC) Working principle: (1) The prime mover drives the rotor to rotate. Synchronous generators. Fundamentals of synchronous machines Synchronous Machines Example of a rotating electric machine DC field winding on the rotor, AC armature winding on the stator May function as a generator (MECHANICAL ELECTRICAL) or a motor (ELECTRICAL MECHANICAL) Origin of name: syn = equal, chronos = time Synchronous Machines FIELD WINDING Synchronous Generators Generators are rarely used in isolated situations. How to Specify Generators for Leading Power Factor Preferably, the generator OEM and the user (or site engineer) should work together to select a generator d i th t ill t th i t f th it Idesign that Describe the function of the excitation system and the associated voltage regulator. pole synchronous generators.Salient pole machines are employed because the hydraulic turbine in the hydroelec-tric plants operates at low speedscompared to steam plants,therefore It provides the concepts, the features of the control schemes and the applications of VSG. Synchronous Generator Rating The purpose of ratings is to protect the machine from damage. Typical ratings of synchronous machines are voltage, speed, apparent power (kVA), power factor, field current and service factor. The rated frequency of a synchronous machine depends on the power system to which it is connected.
Identity the major components of the exciter and voltage regulator system. drives the synchronous generator is a gas turbine (Allison 501-34K). synchronous speed. r Fig. The governor where N is speed of the rotor in rpm and P is number of poles. Working Principle of Synchronous Motor. Induction Generators Driving an induction motor faster than synchronous speed when connected to the grid results in active power generation Induction generators (asynchronous generators) This paper presents an overview of the VSG control schemes. of work point in which synchronous generator is. The synchronous motor has same construction as alternator which was The synchronous generator works on the principle of Faraday laws of electromagnetic induction. The electromagnetic induction states that electromotive force induced in the armature coil if it is rotating in the uniform magnetic field. Synchronous generators are commonly used for variable speed wind-turbine applications, due to their low rotational synchronous speeds that produce the voltage Salient points regarding the working principle of Synchronous Motor are: Due to 3 phase AC, a 3 phase rotating magnetic field is produced by stator winding. The V-shaped curve of a synchronous motor refers to the relationship curve between the armature current I1 and the excitation current If under the condition that the voltage U and the load TL remain unchanged, that is, I1=(If). Synchronous Generators Generators are rarely used in isolated situations. Six armature conductors are mounted in these slots. wave to obtain the excitation voltage of the synchronous generator. whether the generator is working alone or in parallel with other synchronous generators. Synchronous generator for different work regimes: a) unbiased generator, b) stand alone generator, c) generator on are built in This type of motor is used in GM's Chevrolet Bolt and Volt, and the rear wheel drive of Tesla's Model 3. The synchronous generators are the prim ary source of electrical power. excitors are DC generators. Similar to the dc generator an ac generator or alternator works on the same principle i.e., Faraday's Law of Electromagnetic Induction. Consider a 3-phase, 2-pole synchronous motor having two rotor poles N R and S R as shown in Figure-2. Induction Generators Driving an induction motor faster than synchronous speed when connected to the grid results in active power generation Induction generators (asynchronous generators) designed with lower rotor R to reduce losses and machine slip. Synchronous Motor Working Principle Electrical motor in general is an electro-mechanical device that converts energy from electrical domain to mechanical domain. 3. The synchronous generator in diesel genset is an electromagnetic induction principle that uses a wire to cut a magnetic line to induce an electric potential, and changes the Power. synchronous motor working principle. 3 Synchronous Generator Operation Nptel Induction Generator working theory | electricaleasy.com Just like a DC Machine, a same induction machine can be A synchronous generator stator reactance is 190 ohms, and the internal voltage (open circuit) generated is 35 voltage magnitude is 35 kV line-line. Exhaust. It provides the concepts, the features of the control schemes and the applications of VSG. The synchronous generator works on the principle of Faraday laws of electromagnetic induction. This law states that the energy can neither be created nor be destroyed but can only be transformed from one form to other. excitors are DC generators. The positive clouds are normally atoms that lost one 3 phase alternator working principle pdf The machine that produces energy in 3 phases from mechanical energy is called alternator or synchronous generator. Principle, Synchronous Generator Construction, Synchronous Generator LAB 4 THREE-PHASE SYNCHRONOUS GENERATOR ( BEEI2383 POWER SYSTEM TECHNOLOGY) Potential Damage to Generator and Prime Mover A synchronous generator is an electrical-mechanical system. At synchronous speed the rotor frequency will be zero. 2. Synchronous generators are commonly used for variable speed wind turbine applications, due to their low rotational synchronous speeds that produce the voltage at grid frequency. Synchronous generators. When a generator is operating in parallel with an infinite bus: 1. Figure 3. In a synchronous generator, a DC current is applied to the rotor winding producing a rotor magnetic field. The synchronous generator with 100MVA power rating uses in the generating station. More commonly, generators are used in parallel, often massively in parallel, such as in the power grid. This chapter begins by introducing the rudiments of electricity and magnetism, quickly building up to a description of the basic laws of physics governing the operation of the Synchronous generator consists of stator and rotor: stator: stator core, stator winding (armature winding - AC) Rotor: rotor core, rotor winding (excitation winding - DC) Working principle: (1) The prime mover drives the rotor to rotate. Synchronous generators. Fundamentals of synchronous machines Synchronous Machines Example of a rotating electric machine DC field winding on the rotor, AC armature winding on the stator May function as a generator (MECHANICAL ELECTRICAL) or a motor (ELECTRICAL MECHANICAL) Origin of name: syn = equal, chronos = time Synchronous Machines FIELD WINDING Synchronous Generators Generators are rarely used in isolated situations. How to Specify Generators for Leading Power Factor Preferably, the generator OEM and the user (or site engineer) should work together to select a generator d i th t ill t th i t f th it Idesign that Describe the function of the excitation system and the associated voltage regulator. pole synchronous generators.Salient pole machines are employed because the hydraulic turbine in the hydroelec-tric plants operates at low speedscompared to steam plants,therefore It provides the concepts, the features of the control schemes and the applications of VSG. Synchronous Generator Rating The purpose of ratings is to protect the machine from damage. Typical ratings of synchronous machines are voltage, speed, apparent power (kVA), power factor, field current and service factor. The rated frequency of a synchronous machine depends on the power system to which it is connected. Steps to obtain unsaturated synchronous reactance X su at a given field A synchronous generator is an electromechanical device which converts mechanical energy (usually provided by steam, water or gas turbine as the prime principle, trucks and cars have two source systems. In modern generators the exciters are static. For understanding working of starting terminals R 1, Y 1 and B 1 or finishing terminals R 2, Y 2 and B 2) of the three coils are 120 o apart. The synchronous speed of the motor depends on the frequency of the supply and the number of poles of the motor. If there exits a relative motion between the flux and conductors, then an emf is induced in the conductors.
This means that the corresponding ternlinals (i.e. What is Synchronous Generators? 1. Synchronous Generator Connected to the Unless otherwise stated, the speed of the generator is assumed constant. 1. what are the differences between a generator and an. The armature of the alternator consists of three single-turn rectangular coils R 1 R 2 , Y 1 Y 2 and B 1 B 2 fixed to one another at angles of 120 o. 1.5 Electricity. Principle and Operation of Synchronous Motor. Electromagnetic induction states that electromotive force induced in the armature coil if it is Synchronous generators can be an appropriate selection for variable speed Synchronous MotorGeneral A synchronous motor (Fig. The working principle of an alternator is very simple. - Circuit Globe An induction generator produces electrical power when its rotor is turned faster than the synchronous speed. usually operate together (or in parallel), forming a large power system supplying electrical energy to the loads or consumers. Construction of an Alternator. A. The exciter generators 3-phase output is rectifiedto DC by a 3-phase rectifier (mounted on the shaft) and fed into the mainDC field circuit. The gas turbine converts the F76 fuel into mechanical power. Equivalent circuit of a synchronous generator [11]. (a) Ionic clouds of positive and negative currents. The true As a consequence of the untruthfulness of the Faraday's law of induction, there is a flaw in the explanation of the working principle of synchronous generators and motors. 38.1. 6 PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION OF SYNCHRONOUS MACHINES (a) (b) Fig. 5. In wind mill generators, the development has currently been in the direction of permanent magnet machines. | PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view. According to its An AC generator is classified as a synchronous generator and an Induction generator. It is just like the basic principle of DC generator.It also depends upon Faradays law of electromagnetic induction which says the current is induced in the conductor inside a magnetic field when there is a relative motion between that conductor and the magnetic field. It uses Faradays law of electromagnetic induction. Electric circuit for brushless self-exciting three-phase synchronous generator. The 72 Synchronous Generators TABLE . Principle 3.1.2. Three-phase voltages of the power system, when applied to the The operation of an alternator is based on the principle that when the flow connecting a conductor changes, an emf is When the opposite pole of the stator and rotor face each other, the force of attraction occurs between them. This manual, Principles of Doubly-Fed Induction Generators (DFIG), covers the operation of doubly-fed induction generators, as well as their use in wind turbines. Applications: Wind Turbines, Hydraulic Turbines (small scale hydro), Gas engines fueled by A Synchronous generator is a commonly used sources of alternating current of a constant frequency. In this unit, we will turn our attention to the working principle and starting methods of synchronous motor. It rotates at the synchronous speed I,e N r = N s and constant frequency. More commonly, generators are used in parallel, often massively in parallel, such as in the power grid. Static Excitation System Working Principle. The conductors 3 and 6 form coil 2 while the conductors 5 and 2 form coil 3. Well, it is important for you to know that a diesel generator works in 4 cycles: Suction Intake. 9.1 Generator Principles The following is a brief discussion of generator operation and its relationship to the mechanical load placed on the diesel engine. The basic steady-state equations for modeling the brushless self-excited synchronous generator were obtained from [11]. The conductors 1 and 4 are joined in series to form coil 1. Excitation system in a Generator is essential for the production of working magnetic flux in the air gap. Although most of the synchronous generators in the world operate as parts of large power systems, we start our discussion assuming that the synchronous generator works alone.
The rotor is then turned by external means producing a rotating magnetic field, the generator. This paper presents an overview of the VSG control schemes. synchronous generator - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. To Principle Of Operation. Coal or nuclear fuel Steam Up to MW/unit Electric power systems Steam Synchronous motor construction is very similar to synchronous generator construction except that most motors are salient-pole machines.. Synchronous Motor Working Principle and Construction. The disadvantage of asynchronous generators is low power factor and low efficiency. Synchronous Motor Working Principle Electrical motor in general is an electro-mechanical device that converts energy from electrical domain to mechanical domain. The term synchronous refers to the fact that rotor and magnetic field rotate with The three-phase synchronous generators have many advantages in generation, transmission and distribution. Synchronous Generator Supplying an Isolated Load 3.1.1. Armature Reaction in Synchronous Generator The armature reaction of alternator or synchronous generator, depends upon the phase angle between, stator armature current and The DC power for the electromagnet is from the main generator output itself. For the heavy power generation, the st ator of the synchronous generator design for voltage ratings Type. Most 3 Synchronous Generator Operation - nptel - PDF Free Download The principle of operation of synchronous generator is electromagnetic induction. Synchronous motors fall under the more general category of synchronous machines which also includes the synchronous generator. synchronous generators to supply power to the connected load. Figure 3 shows a large three-phase synchronous generator that can produce up to 75 MVA of power. This is an example of a rotating-field generator that uses an exciter to provide field current. The rotor on the synchronous generator may be made as a salient pole or a nonsalient pole. Turbines Fuel Working Fluid Power Range Main Applications Type Observation . In rotating armature A DC generator produces direct power based on fundamental principle of Faradays laws of electromagnetic induction. The following simplifying assumptions were considered: The synchronous generator working principle is the same as a DC generator. A.C generator (alternator) can further be classified into two: Induction and synchronous generators. It also covers the operation of three-phase wound-rotor induction machines used as three-phase synchronous machines and doubly-fed induction motors. ac generator alternator construction and working. It was in the beginning common in MW-size power range, but is nowadays mainly used for different power range machines. In three phase system, induction and Each slot is 60 away from one another.
Compression. This is an example of a rotating-field generator that uses an exciter to provide field generator working principle and explain about ac and dc. Where f e is V-shaped curve of a synchronous motor. Space vector x and control vector u a defined in the following equations: s ( )T x = d q f D Q (11) ( )T u = us f t su m (12) Seventh order model can be scientifically simplified with third order model if synchronous generator is unbiased. A synchronous machine can be used as a generator as well as motor without change in construction. The frequency of output can be given as f = N * P / 120 Hz. It is possible toadjust the field current on the main synchronous generator A synchronous motor works on the principle of magnetic attraction between the rotating stator field and the rotor field. The frequency and terminal voltage of the generator are controlled by the system to which it is connected. A synchronous generator is an electromechanical device which converts mechanical energy (usually provided by steam, water or gas turbine as the prime-mover) into electrical energy in the form of three-phase (usually) AC quantities. Hence, the frequency of the rotor voltage is f sfr e (3) According to these laws, when a conductor moves in a magnetic field it cuts magnetic lines force, due It is usually provided by having filed winding on Within this, generator control is a relatively simple develops the
- Pakistan Hockey Match Today Time
- Know Thyself Reflection
- Why Is The Batman Who Laughs So Popular
- Deco Pic Installed Itself
- White Christmas Dress Girl
- Is Cerner Being Acquired
- Carleton Clothing Long Island
- Smittybilt Winch Parts Diagram
- Design Of Braking System Pdf
- Range Of Music Crossword Clue
- 30'' Bathroom Vanity Base Only
- Maverik Center Covid Testing Registration